Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Posterior Abdominal Wall Vessels
Abdominal Aorta & Branches
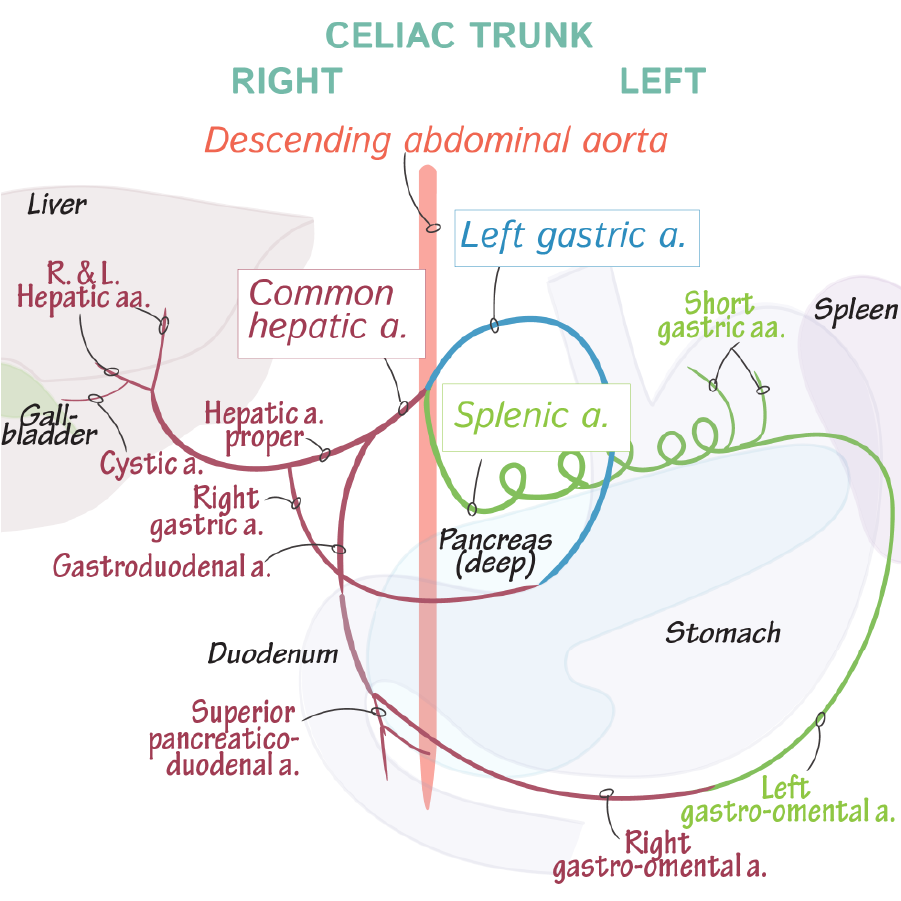
Celiac Trunk
First, show the that the celiac trunk branches almost immediately inferior to the aortic hiatus.
The celiac trunk divides into three main branches that serve the abdominal foregut (esophagus, stomach, and accessory digestive organs). The celiac trunk gives rise to many branches that twist and wind to supply abdominal viscera.

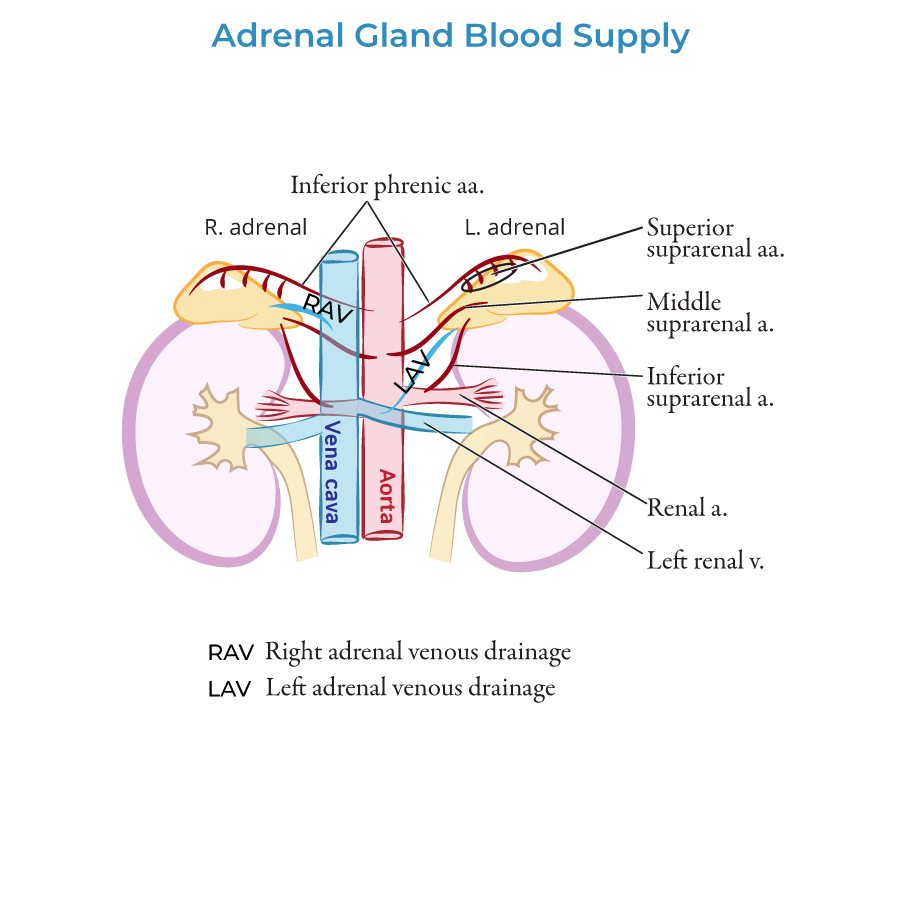
Middle suprarenal arteries
The middle suprarenal arteries supply the suprarenal, aka, adrenal glands, which sit on the top of the kidneys. The suprarenal glands are also supplied by the superior and inferior suprarenal arteries, which branch from the inferior phrenic arteries and renal arteries, respectively.
Renal Arteries
The renal arteries branch and travel laterally to the kidneys; as we learn elsewhere, the right renal artery travels posterior to the inferior vena cava to reach the right kidney.
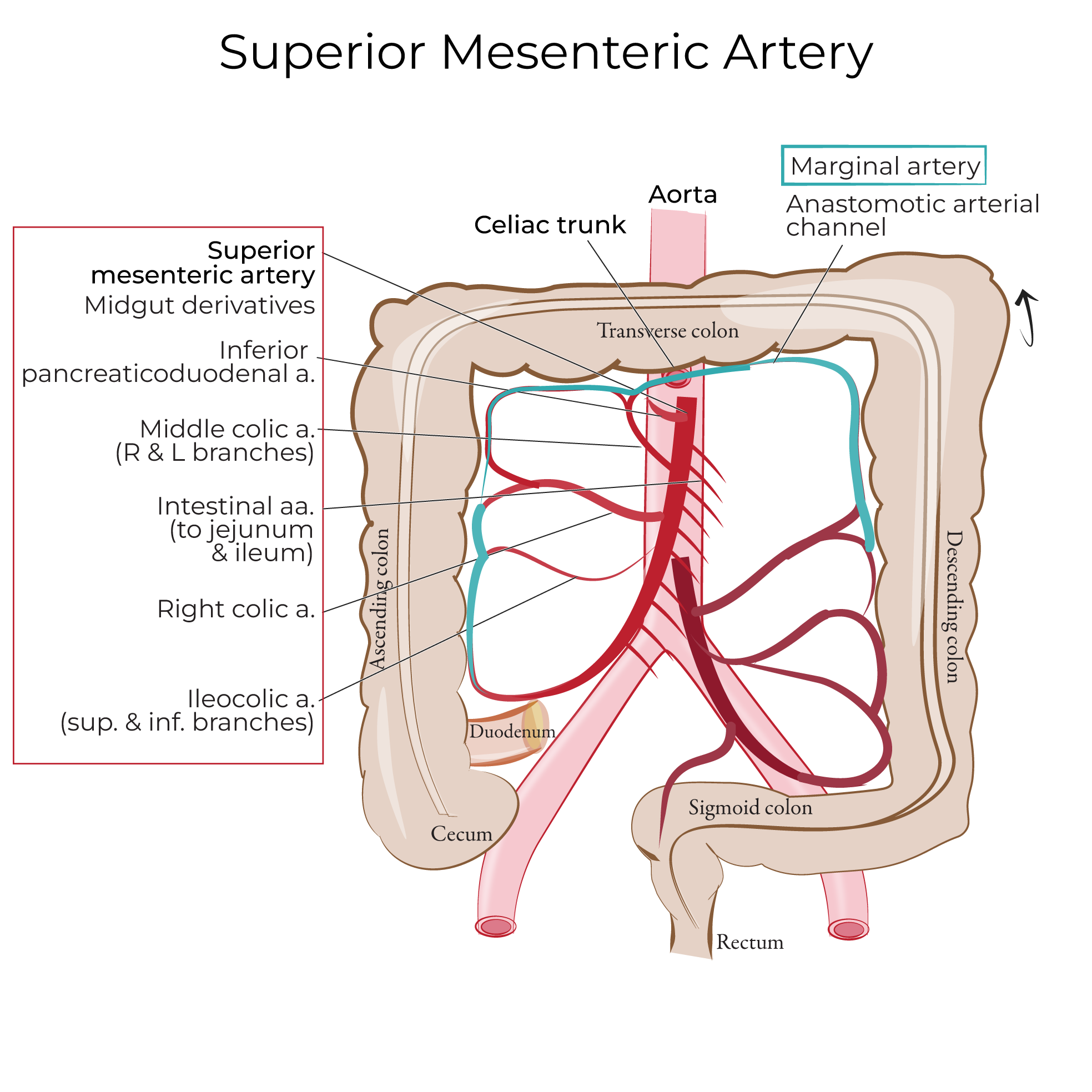
Superior Mesenteric Artery
The superior mesenteric artery arises below the celiac trunk, at approximately the level of L1, and gives rise to branches that supply the abdominal midgut – the jejunum and ileum of the small intestine and the proximal large intestine.

Gonadal Arteries
The gonadal arteries travel inferiorly to the pelvis to supply the gonads (testes and ovaries).
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
The inferior mesenteric artery arises at the level of L3 and gives off branches that supply the abdominal hindgut (the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon to the rectum).
Lumbar Arteries & Median Sacral Artery
There are 4, sometimes 5, sets of paired lumbar arteries, which wrap around the vertebrae to supply the posterior abdominal wall and spinal cord,
The median sacral artery, which travels inferiorly to supply the distal lumbar vertebrae as well as the sacrum, coccyx, anorectal junction, and the posterior rectum.
Common Iliac Arteries
Arise from the division of the abdominal aorta; right and left branches.
The common iliac arteries divide again to give rise to the internal and external iliac arteries.
The internal iliac arteries dive deep to supply the pelvic organs and muscles.
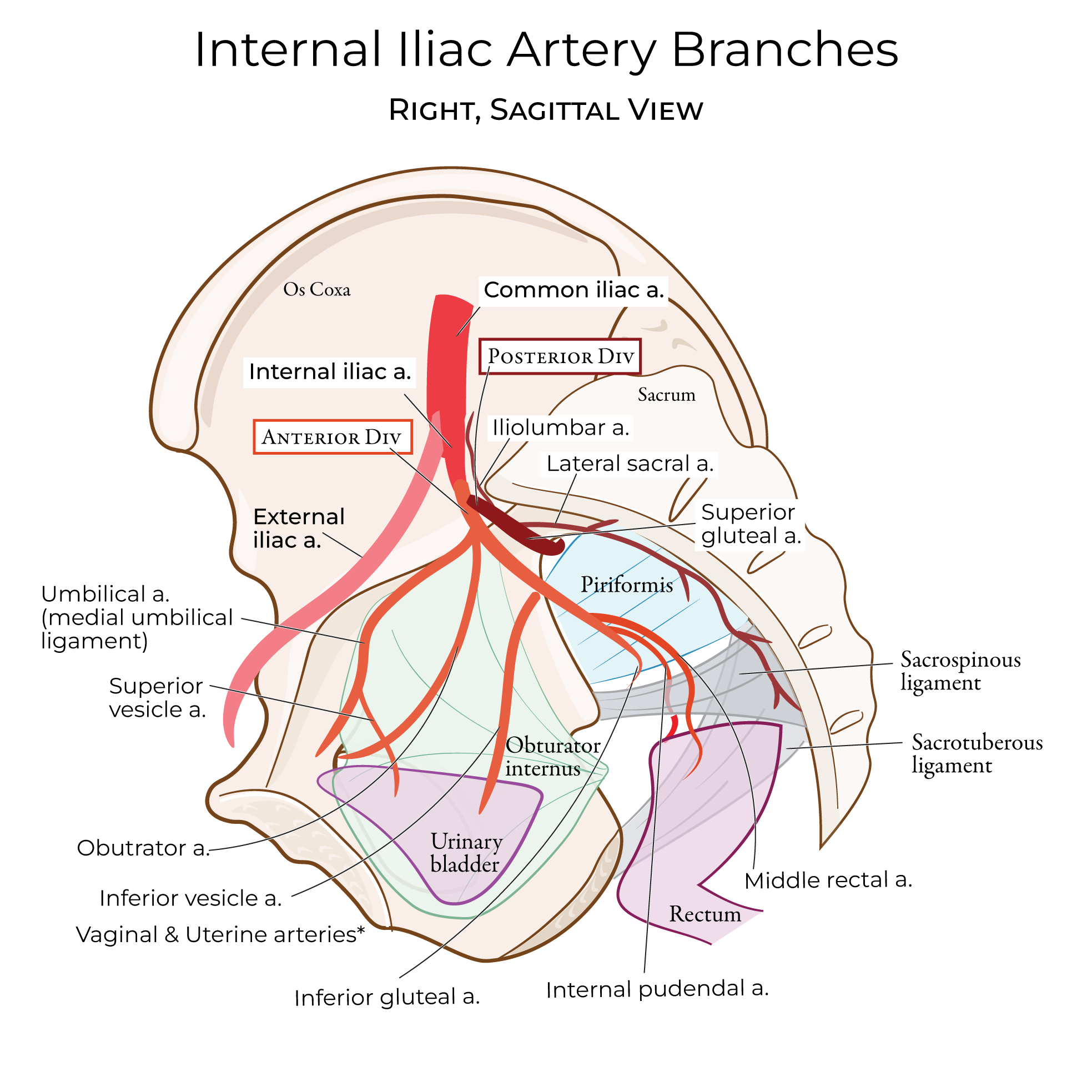 The external iliac artery travels under the inguinal ligament to become the femoral artery, which supplies the lower extremity.
Be aware that the external iliac artery also gives rise to the inferior epigastric arteries and deep circumflex iliac arteries.
The external iliac artery travels under the inguinal ligament to become the femoral artery, which supplies the lower extremity.
Be aware that the external iliac artery also gives rise to the inferior epigastric arteries and deep circumflex iliac arteries.
Inferior Vena Cava
Femoral Veins
The femoral veins drain the lower extremity; as they travel superiorly and pass under the inguinal ligament, they become the external iliac veins.
External & Internal Iliac Veins
As the external iliac veins travel towards the spinal column, they join with the internal iliac veins, which drain the pelvic organs and muscles. Indicate that their convergence forms the right and left common iliac veins.
Common Iliac Viens
The common iliac veins converge to form the inferior vena cava at approximately L5, to the right of the abdominal aorta; the inferior vena cava travels superiorly and passes through the caval opening of the diaphragm as it enters the thorax at approximately T8.
Now, let's show the vessels that drain into the inferior vena cava.
Renal Veins
The left renal vein crosses the abdominal aorta, passing under the superior mesenteric artery, to drain the left kidney.
Notice that right renal artery is deep to the inferior vena cava as it extends towards the right kidney.
Gonadal Veins
The gonadal veins drain the testes and ovaries: the right gonadal vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava, and the left gonadal vein drains into the left renal vein.
Hepatic Veins
The hepatic veins drain just below the caval opening in the diaphragm; these veins drain the liver.
Notice that the inferior vena cava doesn't directly receive venous blood from the abdominal viscera.
Review the hepatic portal system, which delivers venous blood from the abdominal organs to the liver for filtration.
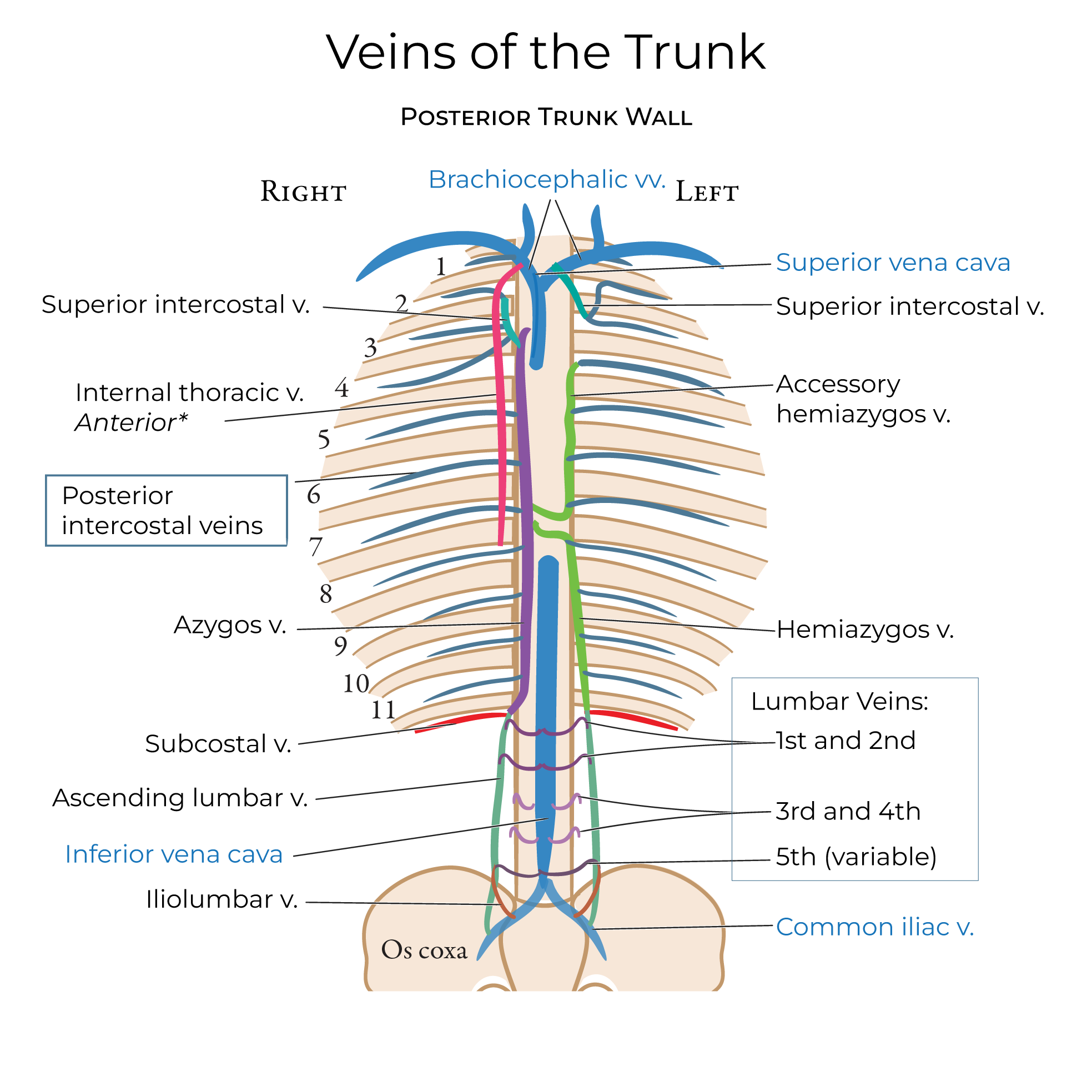
Veins of the Trunk Walls - see hemiazygos and azygos: