USMLE/COMLEX 3 - Small Vessel Vasculitis
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for USMLE Step 3 & COMLEX-USA Level 3 from the Small Vessel Vasculitis tutorial, as well as points of interest at the end of this document that are not directly addressed in this tutorial but should help you prepare for the boards. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
 5. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA):
5. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA):
 6. Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA):
6. Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA):
- --
VITAL FOR USMLE/COMLEX 3
General Concepts of Small Vessel Vasculitis
1. Small vessel vasculitides cause blood vessel inflammation, leading to ischemia, necrosis, and multiorgan dysfunction.
2. Common systemic symptoms: fever, weight loss, fatigue, arthralgias, and skin manifestations like palpable purpura.
3. Initial treatment for most forms is high-dose corticosteroids, with escalation to immunosuppressants for organ-threatening disease.
ANCA-Associated Vasculitides
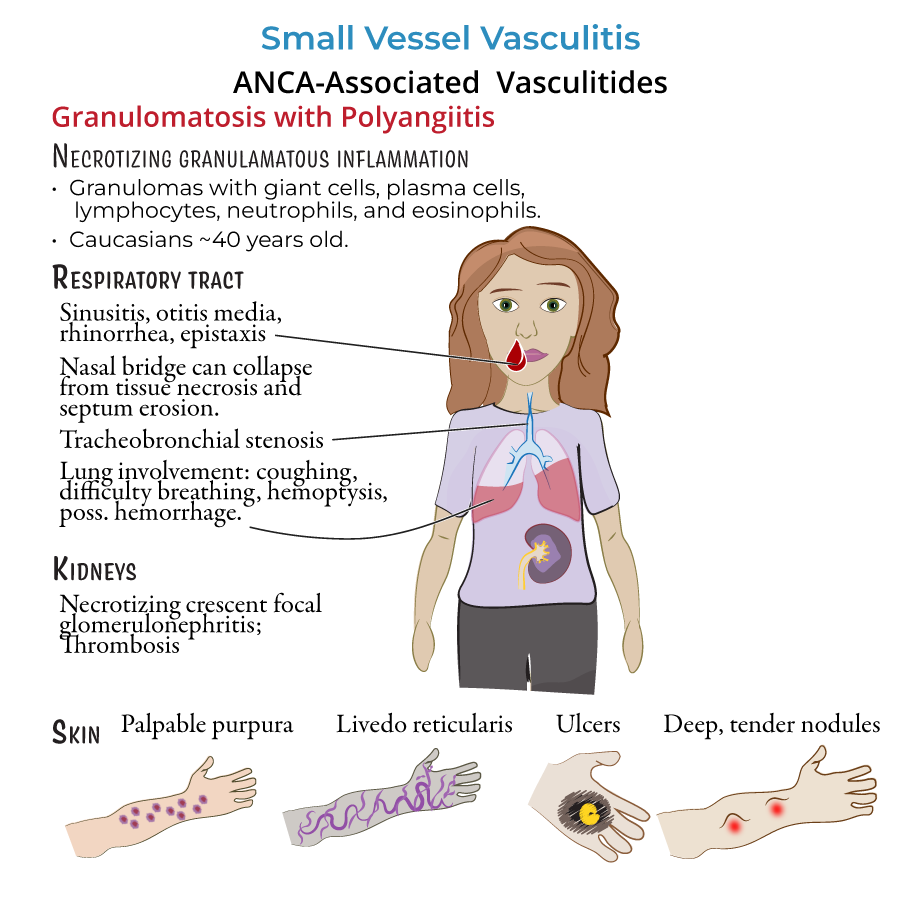
4. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA):
- Classic triad: Upper respiratory, lower respiratory, and renal involvement.
- ENT symptoms: sinusitis, otitis media, nasal septal perforation (saddle-nose deformity).
- Pulmonary: cough, hemoptysis, nodular cavitary lesions on imaging.
- Renal: rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN).
- Skin: palpable purpura, ulcers.
- Laboratory: c-ANCA positive (anti-proteinase 3).
- Treatment: corticosteroids plus rituximab or cyclophosphamide.
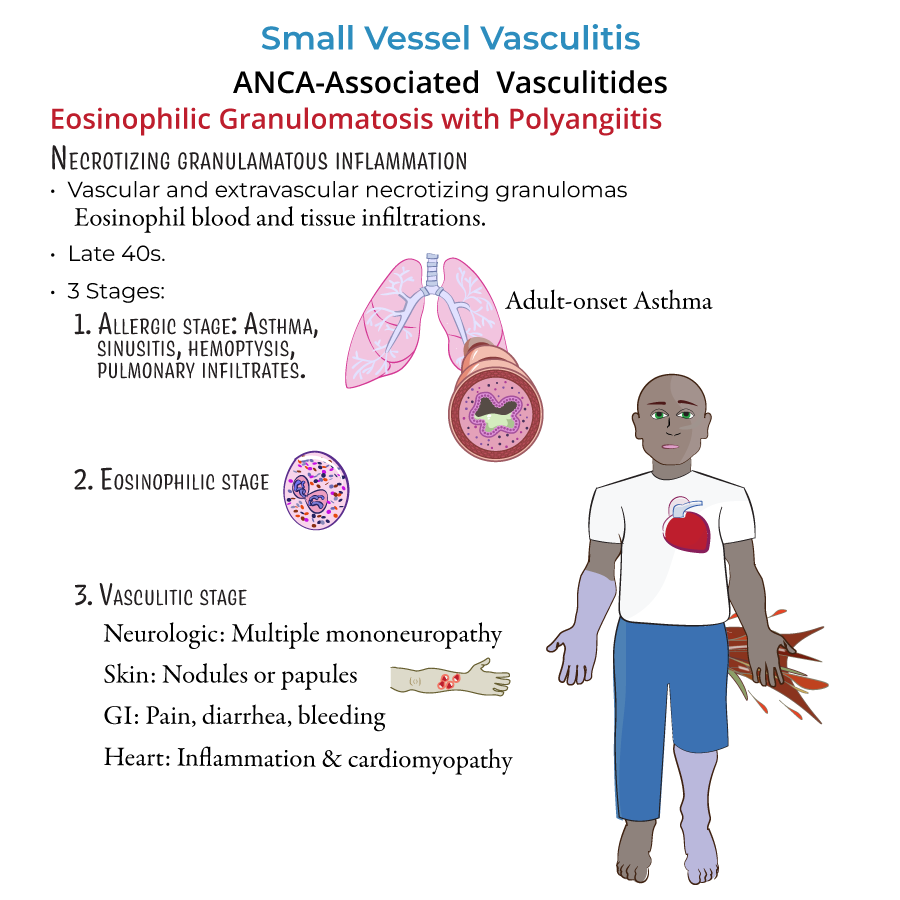
 5. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA):
5. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA):
- Triad: Asthma, eosinophilia, and vasculitis.
- Cardiac involvement (e.g., myocarditis) is a leading cause of death.
- Peripheral neuropathy (mononeuritis multiplex).
- p-ANCA positive (anti-MPO).
- Treatment: corticosteroids alone for mild disease; corticosteroids plus cyclophosphamide or mepolizumab for severe disease.
 6. Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA):
6. Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA):
- Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis and palpable purpura.
- Pulmonary involvement: alveolar hemorrhage possible.
- p-ANCA positive.
- Treatment: corticosteroids plus rituximab or cyclophosphamide.
- --
HIGH YIELD
Non-ANCA Small Vessel Vasculitides
1. IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein Purpura):
- Common in children, can occur in adults.
- Triad:
- Palpable purpura (typically on lower extremities).
- Arthralgias.
- Abdominal pain, GI bleeding.
- Renal involvement (hematuria, IgA nephropathy).
- Preceded by upper respiratory infection.
- Diagnosis is clinical; confirmed by skin biopsy (IgA deposition) if uncertain.
- Management: Supportive for mild disease; corticosteroids for severe renal, GI, or joint involvement.
- Systemic immune-complex vasculitis associated with Hepatitis C.
- Triad:
- Palpable purpura.
- Arthralgia.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Labs:
- Positive cryoglobulins.
- Low complement (especially C4).
- Treatment: Treat underlying HCV infection with antivirals plus immunosuppressive therapy if severe.
- Secondary vasculitis can occur in longstanding disease.
- Monitor for skin ulcers, nephritis, neurologic symptoms.
- --
Beyond the Tutorial
Stepwise Management Strategies
1. GPA and MPA:
- Induction: High-dose corticosteroids plus rituximab or cyclophosphamide.
- Maintenance: Azathioprine, methotrexate, or rituximab.
- Mild (asthma only): corticosteroids alone.
- Severe (cardiac, renal, mononeuritis multiplex): corticosteroids plus cyclophosphamide or IL-5 inhibitor (mepolizumab).
- Start with antiviral therapy if due to Hepatitis C.
- Use corticosteroids if severe or life-threatening disease.
- Supportive in most pediatric cases.
- Adults with severe renal disease: corticosteroids; monitor renal function closely.
Important Complications to Monitor
5. GPA:
- Pulmonary hemorrhage.
- End-stage renal disease.
- Heart failure from eosinophilic myocarditis.
- Pulmonary-renal syndrome (hemoptysis and renal failure).
- Chronic kidney disease, neuropathy.
- Long-term renal impairment in adults.
Key Diagnostic Tools
10. ANCA Testing:
- c-ANCA for GPA.
- p-ANCA for MPA and EGPA.
