USMLE/COMLEX 3 - Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for USMLE Step 3 & COMLEX-USA Level 3 from the Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea tutorial, as well as points of interest at the end of this document that are not directly addressed in this tutorial but should help you prepare for the boards. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
 Below is information not explicitly contained within the tutorial but important for USMLE & COMLEX 3.
Below is information not explicitly contained within the tutorial but important for USMLE & COMLEX 3.
- --
VITAL FOR USMLE/COMLEX 3
Clinical Decision Making
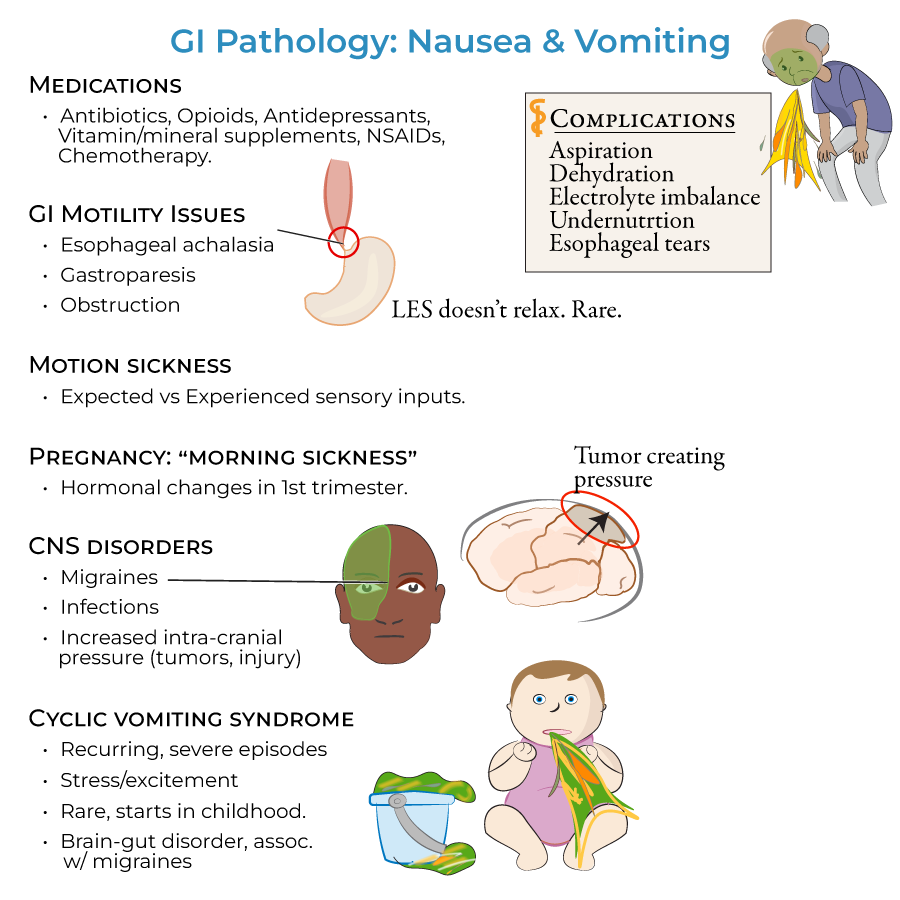
1. Medication review: Identify and manage medication-related causes including antibiotics, opioids, antidepressants, vitamins and mineral supplements, NSAIDs, and chemotherapy
2. Complication assessment: Evaluate and address vomiting complications (aspiration, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, undernutrition, esophageal tears) and diarrhea complications (malabsorption, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances)
Differential Diagnosis - Nausea and Vomiting
1. Obstructive vs. functional: Distinguish mechanical GI obstructions (adhesions, volvulus, foreign bodies, hernias, tumors) from motility disorders (gastroparesis, esophageal achalasia)
2. Neurological etiologies: Identify central nervous disorders (migraines, infections, increased intra-cranial pressure) and vestibular causes (motion sickness)
3. Systemic conditions: Recognize early pregnancy and cyclical vomiting syndrome presentations

Differential Diagnosis - Diarrhea
1. Inflammatory vs. malabsorptive: Differentiate inflammatory bowel disease patterns (Crohn's with mucous diarrhea, ulcerative colitis with bloody diarrhea) from malabsorptive disorders (lactose intolerance, celiac disease)
2. Exocrine dysfunction: Identify pancreatic insufficiency through characteristic steatorrhea (oily, foul-smelling, yellowish floating stools)
3. Neoplastic: Recognize carcinoid syndrome (watery diarrhea with flushing, wheezing, and valvular heart disease)
Management of Combined Syndromes
1. Infectious etiology: Identify and manage gastroenteritis from common pathogens (norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter)
2. Vascular pathology: Recognize intestinal ischemia from mesenteric artery blockage
3. Systemic disorders: Address functional (irritable bowel syndrome) and endocrine causes (thyroid disorders, adrenal insufficiency, diabetes)
- --
HIGH YIELD
Targeted Management Strategies
1. Esophageal achalasia: Approach to heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation from sustained lower esophageal sphincter contraction
2. Gastroparesis: Management of early satiety, heartburn and vomiting resulting from vagus nerve damage
3. Cyclical vomiting syndrome: Therapeutic approach to stress-triggered recurrent vomiting episodes
Special Clinical Scenarios
1. Early pregnancy: Management of nausea/vomiting occurring throughout the day due to first trimester hormonal changes
2. Motion sickness: Preventive and therapeutic approaches for sensory input mismatch
3. Pancreatic insufficiency: Addressing both the steatorrhea and underlying nutritional deficiencies
Management of Complications
1. Aspiration prevention: Strategies to reduce risk in patients with recurrent vomiting
2. Fluid and electrolyte management: Individualized approach based on severity and chronicity
3. Nutritional support: Indications and methods based on underlying etiology
Diagnostic Strategy Selection
1. Microscopic colitis: When to suspect and appropriate diagnostic workup for watery diarrhea
2. Carcinoid syndrome: Comprehensive approach to diagnosis in patients with watery stools, flushing, and wheezing
3. Intestinal ischemia: Urgent evaluation for patients presenting with nausea, vomiting and bloody diarrhea
- --
Beyond the Tutorial
Advanced Management Considerations
1. Refractory cases: Step-up therapy for symptoms unresponsive to first-line interventions
2. Multidisciplinary approach: Integration of gastroenterology, surgery, and nutrition services
3. Emerging therapies: Novel pharmacologic and procedural interventions
System-Based Practice
1. Cost-effective evaluation: Appropriate testing algorithms for common presentations
2. Transitions of care: Inpatient to outpatient management coordination
3. Quality metrics: Reducing readmissions and improving patient outcomes
Patient Safety Considerations
1. Medication reconciliation: Preventing adverse effects and interactions
2. Preventive strategies: Reducing nosocomial infections and complications
3. Patient education: Self-management techniques and return precautions
Special Populations
1. Geriatric patients: Modified assessment and management approaches
2. Immunocompromised hosts: Expanded differential and management considerations
3. Chronic disease management: Long-term care strategies and monitoring
