USMLE/COMLEX 3 - Heart Murmurs
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for USMLE Step 3 & COMLEX 3 from the Hypertension Overview tutorial, as well as points of interest at the end of this document that are not directly addressed in this tutorial but should help you prepare for the boards. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
- --
VITAL FOR USMLE Step 3 & COMLEX 3

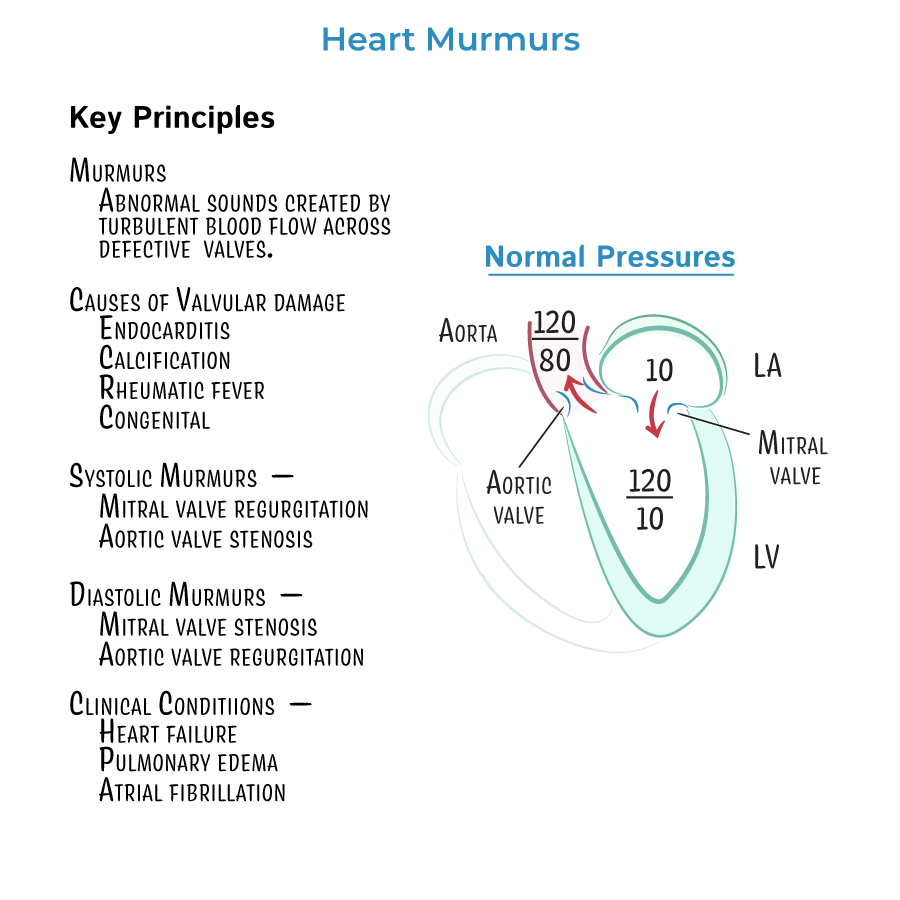
1. Classify Murmurs by Timing
- Systolic murmurs: Aortic stenosis (AS), Mitral regurgitation (MR), Mitral valve prolapse (MVP), Tricuspid regurgitation (TR)
- Diastolic murmurs: Aortic regurgitation (AR), Mitral stenosis (MS)
- Continuous murmur: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
2. Aortic Stenosis (AS)
- Crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur at right upper sternal border, radiates to carotids
- Classic triad: Syncope, Angina, Dyspnea (SAD)
- Echo confirms diagnosis and severity
- Valve replacement if:
- Symptomatic
- EF <50%
- Undergoing other cardiac surgery
3. Mitral Regurgitation (MR)
- Holosystolic murmur at apex, radiates to axilla
- Causes: ischemic heart disease (papillary muscle rupture), endocarditis, MVP
- Chronic MR leads to LA enlargement and atrial fibrillation
- Management:
- Medical: ACEi, diuretics, beta blockers (if HF)
- Surgical: severe MR + symptoms or EF <60%
4. Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP)
- Mid-systolic click with late systolic murmur
- ↑ with Valsalva (↓ preload)
- Seen in young women and connective tissue disorders
- Usually benign; may progress to MR
5. Aortic Regurgitation (AR)
- Early diastolic murmur at left sternal border, best heard sitting up and leaning forward
- Features: widened pulse pressure, Corrigan's sign, bounding pulses
- Causes: endocarditis, aortic root dilation, congenital
- Management:
- Medical: ACEi/ARB, nifedipine
- Surgery if symptomatic or EF <55%
6. Mitral Stenosis (MS)
- Opening snap + diastolic rumble best at apex in left lateral decubitus
- Most common cause: Rheumatic fever
- Symptoms: exertional dyspnea, hemoptysis, atrial fibrillation
- Echo: LAE, pulmonary HTN
- Treatment: rate control (if AF), diuretics, valvuloplasty if severe symptoms
7. Hypertensive Emergency with Murmur
- If a diastolic murmur is present in a hypertensive patient, suspect aortic dissection
- Next step: Immediate TEE or CTA chest
8. Murmur Maneuver Differentiation (Management Clue)
- Valsalva/Standing: ↓ preload → ↑ HOCM, MVP
- Squatting/Leg raise: ↑ preload → ↑ most murmurs except MVP and HOCM
- These help guide dynamic auscultation findings during exam and clue to etiology
9. When to Refer for Surgery
- Severe symptomatic stenosis or regurgitation
- LV dysfunction thresholds:
- MR: EF <60% or LVESD >40 mm
- AR: EF <55% or LVESD >50 mm
- Always consider valve replacement or repair if undergoing other cardiac surgery
10. Prosthetic Valve Evaluation
- Regular echocardiograms to assess function
- INR targets if on mechanical valves:
- Aortic valve: 2.0–3.0
- Mitral valve: 2.5–3.5
- --
HIGH YIELD
11. Mitral Stenosis in Pregnancy
- Plasma volume increase → exacerbation of MS
- Treat with beta blockers, diuretics
- Avoid volume overload
- Severe MS: balloon valvotomy
12. Endocarditis Considerations
- New murmur + fever = suspect infective endocarditis
- Most commonly affects regurgitant valves
- Use TEE for prosthetic valves or poor TTE windows
- Empiric antibiotics → then tailored post cultures
13. Echocardiogram Use
- TTE is first-line to evaluate murmur
- TEE used for:
- Poor TTE windows
- Suspected endocarditis
- Aortic dissection
- Prosthetic valve evaluation
14. Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
- Surgery indicated if:
- EF <50%
- Abnormal response to exercise stress test
- Elevated gradient or rapid progression
15. Stroke Risk in MS
- Atrial enlargement → atrial fibrillation
- Indication for anticoagulation (warfarin preferred in valvular AF)
- --
Beyond the Tutorial
16. Antibiotic Prophylaxis
- Only for:
- Prosthetic valve
- Prior endocarditis
- Certain congenital heart diseases
- Dental procedures with gingival manipulation
- Use: Amoxicillin 2 g PO 30–60 min before procedure
17. Risk Stratification
- Severe MR with LV dilatation or AF → early surgery
- AS in elderly → careful risk-benefit assessment
- Use STS or EuroSCORE to assess perioperative risk
