USMLE/COMLEX 2 - ECG
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for USMLE Step 2 CK & COMLEX-USA Level 2 from the Electrocardiogram/ECG, EKG tutorial, focusing on clinical application, interpretation, and management that are essential for these exams. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
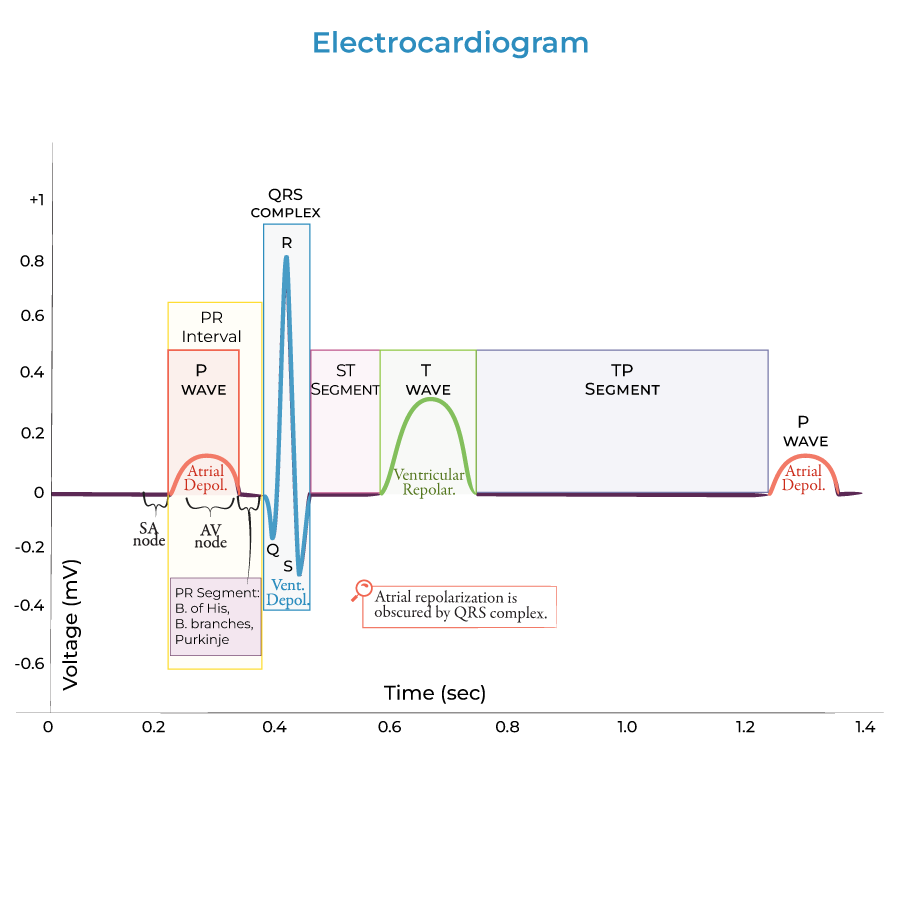 2. Normal Parameters & Deviations:
Below is information not explicitly contained within the tutorial but important for USMLE Step 2 CK & COMLEX Level 2.
2. Normal Parameters & Deviations:
Below is information not explicitly contained within the tutorial but important for USMLE Step 2 CK & COMLEX Level 2.
- --
VITAL FOR USMLE/COMLEX 2
ECG Fundamentals & Clinical Application
1. Basic Components & Clinical Relevance:
- Waves: P (atrial depolarization), QRS (ventricular depolarization), T (ventricular repolarization), U (occasionally present)
- Segments: PR, ST (clinically significant for diagnosing ischemia/infarction)
- Intervals: PR, QT (critical for assessing conduction and repolarization abnormalities)
 2. Normal Parameters & Deviations:
2. Normal Parameters & Deviations:
- PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds (prolongation indicates AV conduction block)
- QRS duration: <0.12 seconds (widening suggests bundle branch block or ventricular origin)
- QT interval: Heart rate dependent (prolongation associated with increased risk of arrhythmias)
- SA node dysfunction presents as inappropriate bradycardia or sinus pauses
- AV nodal disease manifests as varying degrees of heart block
- Bundle branch pathology produces characteristic wide QRS morphologies
- Calculate using PP or RR intervals
- Clinical significance of bradycardia (<60 bpm) and tachycardia (>100 bpm)
Cardiac Conduction System & Rhythm Analysis
1. Normal Conduction Sequence:
- Sinoatrial (SA) node → atria → AV node → bundle of His → bundle branches → Purkinje fibers → ventricular myocardium
- Functional significance: Ensures coordinated contraction from apex to base
- Regularity: Consistent RR intervals indicate regular rhythm
- Rate: Normal (60-100 bpm), bradycardia (<60 bpm), tachycardia (>100 bpm)
- P wave: Present before each QRS in normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval: Consistent in normal conduction
- Normal sinus rhythm: Regular P waves with normal PR interval and rate
- Sinus tachycardia: Rate >100 bpm with normal P wave morphology
- Sinus bradycardia: Rate <60 bpm with normal P wave morphology
- First-degree: Prolonged PR interval (>0.20 seconds)
- Second-degree: Intermittent failure of AV conduction (Mobitz I/Wenckebach or Mobitz II)
- Third-degree (complete): No relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
ECG Interpretation in Ischemia & Infarction
1. Ischemic Changes:
- ST segment depression: Subendocardial ischemia
- T wave inversion: Myocardial ischemia or strain
- ST segment elevation: Transmural injury/infarction
- Hyperacute T waves → ST elevation → Q wave development → T wave inversion → resolution of ST elevation
- Timeline of changes helps determine infarct age
- Anterior: V1-V4 (left anterior descending artery)
- Lateral: I, aVL, V5-V6 (left circumflex artery)
- Inferior: II, III, aVF (right coronary artery)
- Posterior: Tall R waves and ST depression in V1-V2 (reciprocal changes)
ECG in Electrolyte Abnormalities & Drug Effects
1. Potassium Abnormalities:
- Hyperkalemia: Tall, peaked T waves → widened QRS → sine wave pattern
- Hypokalemia: U wave prominence, ST depression, flattened T waves
- Hypercalcemia: Shortened QT interval
- Hypocalcemia: Prolonged QT interval
- Hypomagnesemia: Prolonged QT, U waves, increased risk of torsades de pointes
- Digoxin: "Scooped" ST segments (Salvador Dali mustache), shortened QT
- Antiarrhythmics: Various effects on intervals and repolarization
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Prolonged QRS, rightward axis, terminal R wave in aVR
- --
HIGH YIELD
Systematic ECG Interpretation Approach
1. Rate & Rhythm Assessment:
- Calculate heart rate (300 ÷ number of large boxes between consecutive R waves)
- Assess regularity of rhythm (consistent vs. variable RR intervals)
- Identify P waves and their relationship to QRS complexes
- PR interval: Normal (0.12-0.20 sec), prolonged (>0.20 sec), shortened (<0.12 sec)
- QRS duration: Normal (<0.12 sec), prolonged (>0.12 sec)
- QT interval: Corrected for heart rate (QTc)
- Normal axis: +90° to -30°
- Left axis deviation: -30° to -90°
- Right axis deviation: +90° to +180°
- Clinical significance and associated conditions
- P wave: Size, shape, and orientation
- QRS complex: Configuration in different leads
- ST segment: Elevation, depression, or normal
- T wave: Normal vs. abnormal morphology
- --
Beyond the Tutorial
Advanced ECG Interpretation in Special Populations
1. Pediatric ECG Differences: Age-specific normal values, lead placement, and common abnormalities.
2. Geriatric Considerations: Higher prevalence of conduction abnormalities, effects of comorbidities, and medication interactions.
3. Pregnancy-Related Changes: Physiologic left axis deviation, increased heart rate, and occasional benign arrhythmias.
4. Athletes: Physiologic bradycardia, early repolarization, and increased QRS voltage mimicking pathology.
5. Specific Disease States: Characteristic ECG findings in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, infiltrative diseases, and pulmonary hypertension.
ECG in Perioperative and Critical Care Management
1. Pre-operative Risk Assessment: ECG abnormalities that increase perioperative risk and require further evaluation.
2. Continuous Monitoring Indications: When to use continuous ECG monitoring vs. intermittent assessment.
3. Post-cardiac Surgery Patterns: Expected changes after CABG, valve replacement, and transplantation.
4. Mechanical Ventilation Effects: Impact of positive pressure ventilation on ECG appearance.
5. Extracorporeal Support: ECG considerations during ECMO and other mechanical support devices.
Clinical Management Based on ECG Findings
1. Emergent Interventions:
- ST-elevation MI: Immediate reperfusion (PCI or thrombolytics)
- Unstable bradyarrhythmias: Temporary pacing
- Hemodynamically unstable tachyarrhythmias: Cardioversion
- Non-ST elevation MI: Antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, risk stratification
- Prolonged QT interval: Correction of underlying causes, avoidance of QT-prolonging medications
- First-degree AV block: Usually requires observation only
- Second-degree Mobitz I: Monitoring for progression
- Second-degree Mobitz II and third-degree block: Often require pacemaker
- Rate control for atrial fibrillation
- Antiarrhythmic therapy for recurrent symptomatic arrhythmias
ECG-Guided Therapeutic Interventions
1. Antiarrhythmic Drug Selection: Using ECG features to guide appropriate pharmacologic therapy.
2. Cardioversion Protocols: Indications, contraindications, and procedural management.
3. Temporary Pacing Indications: When to implement transcutaneous, transvenous, or epicardial pacing.
4. Permanent Pacemaker Programming: Rate responsiveness, sensing parameters, and mode selection based on ECG findings.
5. Ablation Therapy Decision-Making: Identifying arrhythmia mechanisms amenable to catheter ablation.
Integrated Assessment with Other Cardiac Testing
1. Echocardiographic Correlation: Integrating ECG findings with structural and functional echocardiographic data.
2. Cardiac Biomarker Integration: Combining ECG changes with troponin and other biomarkers in ACS assessment.
3. Exercise Stress Testing: Interpreting stress-induced ECG changes and their clinical significance.
4. CT and MRI Correlation: Relating ECG abnormalities to advanced imaging findings.
5. Nuclear Imaging Integration: Using ECG to guide interpretation of perfusion studies.
Quality & Safety Considerations in ECG Interpretation
1. Mimics of Ischemia: Conditions that can produce ST-T changes simulating ischemia (LVH, BBB, electrolyte abnormalities).
2. Technical Factors Affecting Interpretation: Lead misplacement, artifact, and improper calibration.
3. Critical Value Communication: Protocols for urgent notification of life-threatening ECG findings.
4. Documentation Standards: Requirements for complete and accurate ECG interpretation documentation.
5. Quality Improvement Strategies: Measures to improve ECG interpretation accuracy and reduce diagnostic errors.
