Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis for USMLE Step 1
Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis for the USMLE Step 1 Exam
Chlamydia
- Etiology:
- Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, an obligate intracellular bacterium. Serotypes D-K are responsible for urogenital infections.
- Epidemiology:
- Most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the U.S., especially among young adults (ages 15–24).
- Clinical Presentation:
- Men: Often asymptomatic; symptomatic cases show urethritis with dysuria and mucoid or clear urethral discharge.
- Women: Commonly asymptomatic; symptomatic cases include cervicitis (mucopurulent discharge) and urethritis. Complications include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
- Diagnosis:
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT): Gold standard, performed on urine or swabs from genital sites.
- Treatment:
- Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days or Azithromycin 1 g single dose.
- Partner treatment is essential to prevent reinfection.
Gonorrhea
- Etiology:
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus.
- Epidemiology:
- Commonly co-infects with chlamydia, particularly in young adults aged 15–24.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Men: Urethritis with purulent discharge and dysuria; may lead to epididymitis.
- Women: Often asymptomatic; symptomatic cases may show cervicitis, PID, and urethritis.
- Extragenital Manifestations: Pharyngeal and rectal infections from oral and anal sex; ocular infections can occur in neonates (ophthalmia neonatorum).
- Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI): Bacteremia presenting with dermatitis-arthritis syndrome, tenosynovitis, and septic arthritis.
- Diagnosis:
- NAAT: Preferred for urogenital, pharyngeal, and rectal specimens.
- Gram Stain: Useful in symptomatic men, showing gram-negative intracellular diplococci.
- Treatment:
- Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM single dose; if chlamydia co-infection is suspected, add doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days.
- Partner treatment is crucial to prevent reinfection.
Syphilis
- Etiology:
- Caused by Treponema pallidum, a spirochete bacterium.
- Clinical Stages:
- Primary Syphilis:
- Painless chancre at the site of infection, typically genital, which heals spontaneously within weeks.
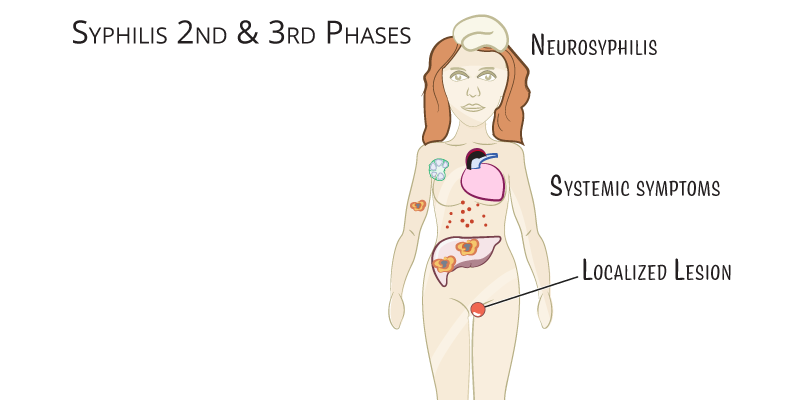
- Secondary Syphilis:
- Systemic symptoms with a maculopapular rash (often on palms and soles), condylomata lata, lymphadenopathy, and mucosal lesions.
- Latent Syphilis:
- Asymptomatic infection that follows secondary syphilis, divided into early latent (within 1 year) and late latent (after 1 year).
- Tertiary Syphilis:
- Late-stage disease with severe complications, including cardiovascular (aortitis) and neurosyphilis (Tabes dorsalis, general paresis), and gummas (granulomatous lesions in various tissues).

- Diagnosis:
- Nontreponemal Tests: Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) or venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test, used for screening and to monitor treatment response.
- Treponemal Tests: Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) or T. pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA) for confirmation; these tests remain positive for life.
- Treatment:
- Primary, Secondary, and Early Latent Syphilis: Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM single dose.
- Late Latent and Tertiary Syphilis (without neurosyphilis): Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM weekly for 3 weeks.
- Neurosyphilis: Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 18–24 million units per day IV for 10–14 days.
Key Points
- Chlamydia:
- Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and often asymptomatic, particularly in women.
- Can cause PID and infertility if untreated.
- Diagnosed by NAAT and treated with doxycycline or azithromycin.
- Partner treatment is essential to prevent reinfection.
- Gonorrhea:
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, commonly co-infecting with chlamydia.
- Presents as urethritis in men and is often asymptomatic in women.
- Diagnosed by NAAT and treated with ceftriaxone, plus doxycycline if chlamydia is co-infected.
- Treating partners is necessary to prevent reinfection.
- Syphilis:
- Caused by Treponema pallidum, with stages: primary (chancre), secondary (rash, systemic), latent, and tertiary (cardiovascular and neurosyphilis).
- Diagnosed with nontreponemal and treponemal tests.
- Treated with penicillin, with follow-up serology and partner treatment to prevent transmission.
