Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
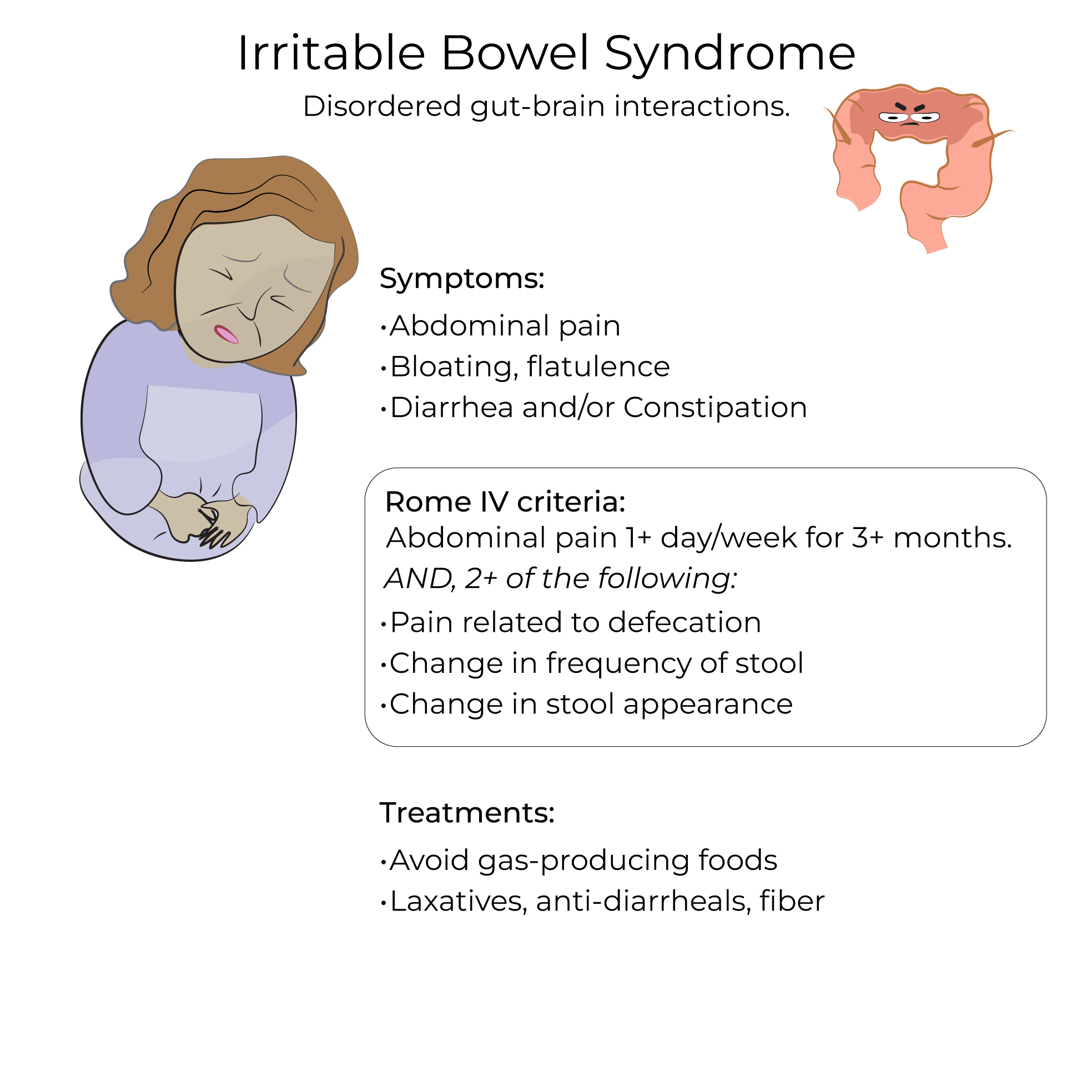
Etiologies are uncertain, but IBS may be due to: abnormal intestinal motility; hypersensitivity of the nerves in the gut in response to to colonic gas, bloating; intestinal inflammation.
Constipation or diarrhea may predominate, or may be "mixed" type.
Exacerbations may be triggered by stress, medications, foods, hormones.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Patients experience constipation and diarrhea with abdominal pain.
Pain occurs an average of at least 1 day per week, associated with at least 2 of the following:
- Defecation can improve or worsen abdominal pain
- Change in defecation frequency
- Change in stool appearance
DIAGNOSIS
Rule out other etiologies; no specific objective exam or lab signs.
TREATMENTS
Lifestyle changes
- Increase dietary fiber, supplement with psyllium, methylcellulose, wheat dextrin.
- Avoid foods that produce excess gas (beans, cabbage, onions, etc).
- Poorly absorbed, fermentable, monosaccharides, and short-chain carbohydrates - FOD-MAPs exacerbate bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea:
- Reduce stress.
Pharmacologic treatments
Medications are used in moderate to severe cases where lifestyle changes do not suffice.
- Abdominal pain: Antispasmodics.
- Constipation: lubiprostone, linaclotide, similar drug (increase fluid secretion and colonic transit).
- Diarrhea: loperamide, bile sequestrants, serotonin 3 receptor antagonist (beware ischemic colitis).
