Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis for NP
Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis for the Nurse Practitioner Licensing Exam
Chlamydia
- Etiology:
- Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, an intracellular bacterium with serotypes D–K responsible for urogenital infections.
- Epidemiology:
- The most common bacterial STI in the U.S., especially affecting people aged 15–24 years.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Men: Often asymptomatic; symptomatic cases present with urethritis, dysuria, and clear or mucoid discharge.
- Women: Often asymptomatic; symptomatic cases may present with cervicitis, urethritis, or PID, leading to chronic pain, infertility, or ectopic pregnancy.
- Diagnosis:
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test): Preferred diagnostic test, performed on urine or swabs.
- Treatment:
- Doxycycline 100 mg PO twice daily for 7 days or Azithromycin 1 g PO single dose.
- Partner treatment is essential to prevent reinfection.
Gonorrhea
- Etiology:
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Men: Urethritis with purulent discharge, dysuria; can progress to epididymitis.
- Women: Often asymptomatic; symptomatic cases may present with cervicitis or PID.
- Extragenital Sites: Pharyngeal and rectal infections; neonatal conjunctivitis in infants.
- Diagnosis:
- NAAT: Recommended for genital and extragenital sites.
- Gram Stain: Useful in symptomatic men, showing gram-negative diplococci.
- Treatment:
- Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM single dose; add doxycycline for chlamydia co-infection.
- Partner treatment is required to prevent reinfection.
Syphilis
- Etiology:
- Caused by Treponema pallidum, a spirochete.
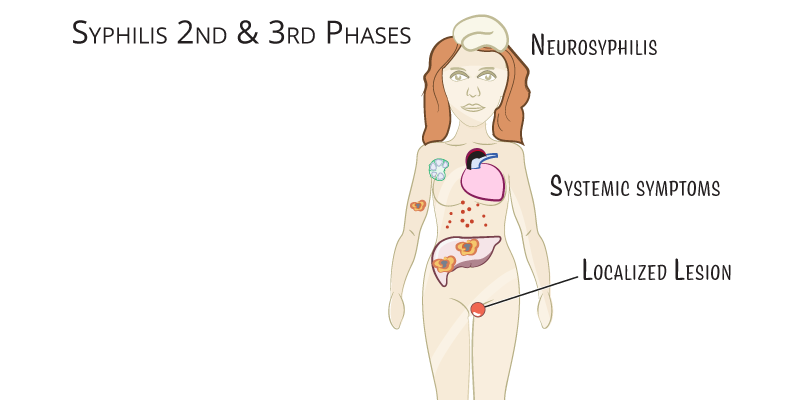
- Clinical Stages:
- Primary: Painless chancre at infection site.
- Secondary: Systemic symptoms, maculopapular rash, condylomata lata.
- Latent: Asymptomatic phase.
- Tertiary: Cardiovascular, neurologic symptoms, and gummas.

- Diagnosis:
- Nontreponemal Tests (RPR, VDRL) for screening.
- Treponemal Tests (FTA-ABS, TPPA) for confirmation.
- Treatment:
- Primary, Secondary, Early Latent: Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM single dose.
- Neurosyphilis: Penicillin G IV for 10–14 days.
Key Points
Chlamydia: Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis*, often asymptomatic, diagnosed by NAAT, treated with doxycycline or azithromycin; partner treatment is critical.
Gonorrhea: Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae*, often asymptomatic in women, diagnosed by NAAT, treated with ceftriaxone (add doxycycline for chlamydia); partner treatment required.
Syphilis: Caused by Treponema pallidum*, presenting in stages (primary, secondary, latent, tertiary); diagnosed by serologic tests and treated with penicillin.
