Allergy & Hypersensitivity for NP
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Allergy for the Nurse Practitioner Licensing Exam
Allergy Overview
- Definition:
- Allergies are hypersensitivity reactions where the immune system responds excessively to typically harmless antigens (allergens), often through IgE-mediated mechanisms.
- IgE antibodies sensitize mast cells and basophils, releasing histamine and other mediators upon re-exposure to the allergen.
- Common Allergens:
- Environmental: Pollens, dust mites, animal dander, and molds.
- Food: Includes peanuts, shellfish, tree nuts, milk, and eggs.
- Medications: Commonly antibiotics like penicillin and NSAIDs.
- Insect Stings: Hymenoptera (e.g., bees, wasps).
- Occupational: Latex, certain chemicals in specific workplace settings.
Clinical Presentations
- Allergic Rhinitis:
- Symptoms: Sneezing, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and itchy eyes; often seasonal.
- Treatment: Intranasal corticosteroids, antihistamines, and allergen avoidance.
- Asthma:
- Symptoms: Cough, wheezing, dyspnea, and chest tightness, often allergen-triggered.
- Treatment: Inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and leukotriene receptor antagonists.
- Atopic Dermatitis:
- Symptoms: Pruritic, erythematous rash on flexural surfaces.
- Treatment: Emollients, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of known irritants.
- Food Allergy:
- Symptoms: Urticaria, angioedema, gastrointestinal symptoms, and anaphylaxis in severe cases.
- Treatment: Strict avoidance of the allergen; epinephrine autoinjector for severe reactions.
- Anaphylaxis:
- Symptoms: Rapid onset with urticaria, angioedema, hypotension, and bronchospasm.
- Treatment: Immediate intramuscular epinephrine, followed by antihistamines and corticosteroids. Patients should carry an epinephrine autoinjector.
Diagnostic Testing
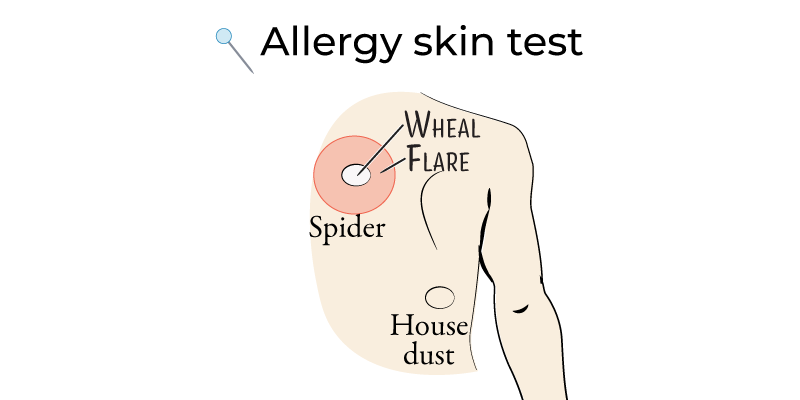
- Skin Prick Testing:
- Introduces allergens into the skin; a positive response shows a wheal-and-flare reaction.
- Used to diagnose allergic rhinitis, asthma triggers, and food allergies.

- Serum IgE Testing:
- Measures specific IgE antibodies, useful for patients who cannot undergo skin testing.
Key Points
- Allergies are immune-mediated, often IgE-driven, and can present with respiratory, skin, and systemic symptoms.
- Diagnosis relies on history, clinical examination, and tests like skin prick or serum IgE testing.
- Management includes allergen avoidance, pharmacologic treatment (e.g., antihistamines, corticosteroids), and immunotherapy for severe cases.
- Anaphylaxis requires immediate epinephrine, and patients at risk should always have an epinephrine autoinjector.
