NCLEX - Small Vessel Vasculitis
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for NCLEX from the Small Vessel Vasculitis tutorial, as well as points of interest at the end of this document that are not directly addressed in this tutorial but should help you prepare for the boards. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
 #
# #
#
- --
VITAL FOR NCLEX
General Concepts of Vasculitis
1. Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels leading to ischemia, necrosis, and organ damage.
2. Common general symptoms include fever, fatigue, weight loss, joint pain, and skin changes (especially palpable purpura).
3. Initial treatment often includes high-dose corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and prevent complications.
4. Nursing priorities focus on monitoring for organ dysfunction (e.g., lungs, kidneys) and preventing infection during immunosuppressive therapy.
- --
HIGH YIELD
Specific Small Vessel Vasculitides
#
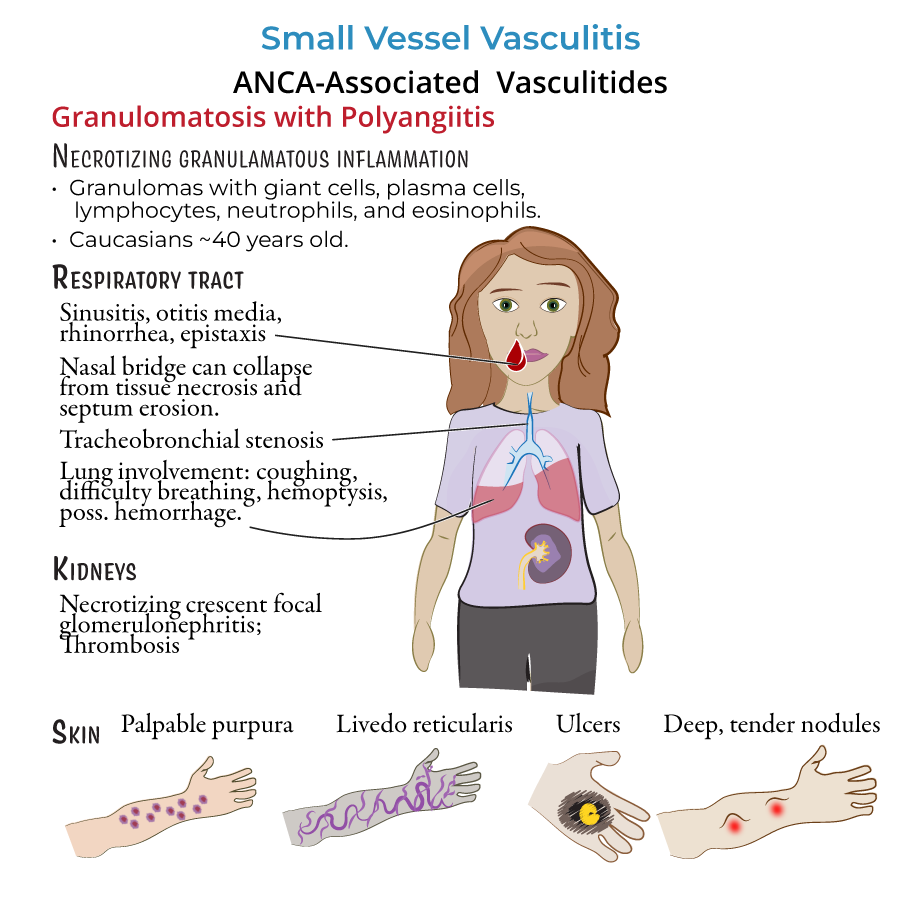
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)
1. Affects nose, lungs, and kidneys.
2. Symptoms:
- Sinusitis, nasal crusting, nosebleeds.
- Cough, shortness of breath, hemoptysis.
- Kidney damage (hematuria, elevated creatinine).
- Skin signs like purpura.
- Monitor for respiratory distress.
- Watch for signs of kidney failure.
- Support corticosteroid administration and infection prevention.
 #
#
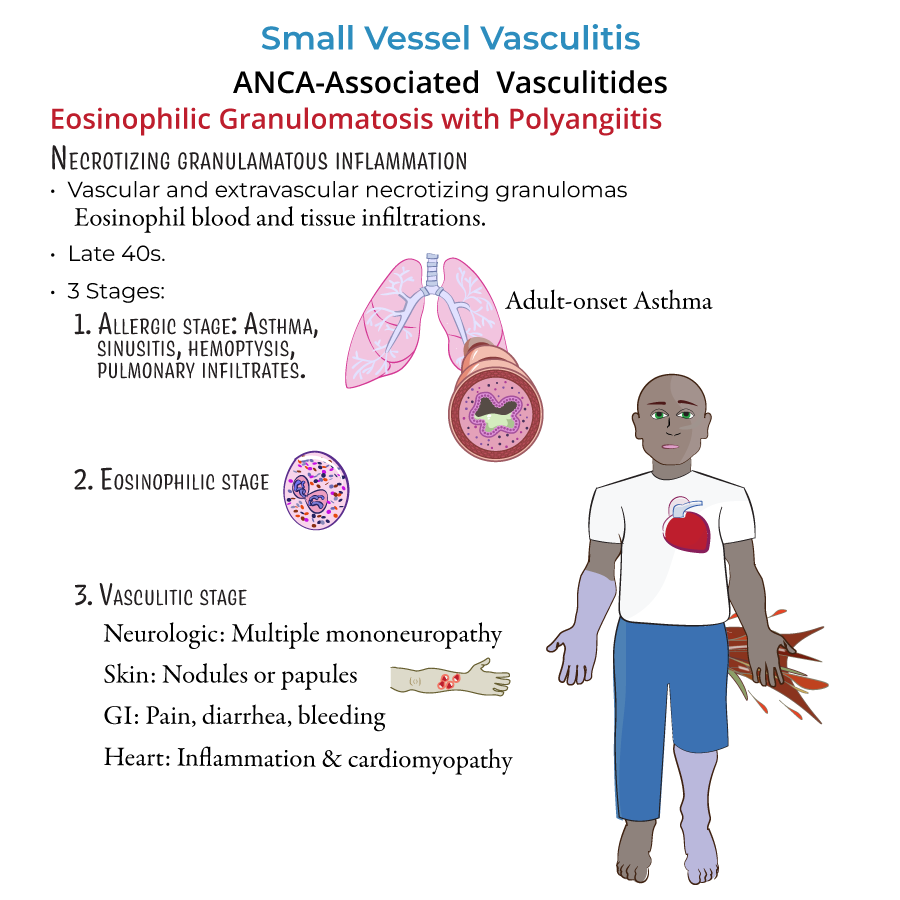
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA)
4. Typically seen in patients with asthma and allergic symptoms.
5. Symptoms:
- Severe asthma attacks.
- Peripheral neuropathy (weakness, numbness).
- Cardiac symptoms (chest pain, heart failure signs).
- Prioritize airway management.
- Monitor heart function closely.
- Watch for new neurologic deficits.
 #
#
Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA)
7. Symptoms:
- Rapid kidney decline (RPGN).
- Purpura on skin.
- Possible pulmonary hemorrhage (coughing up blood).
- Monitor respiratory and renal function.
- Early recognition of hemoptysis is critical.
IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein Purpura)
9. Most common in children.
10. Symptoms:
- Palpable purpura (especially on buttocks and legs).
- Abdominal pain, GI bleeding.
- Joint pain.
- Blood in urine (hematuria).
- Monitor for signs of kidney damage.
- Educate parents that this usually resolves but may need monitoring if kidney involvement is severe.
Cryoglobulinemia
12. Associated with hepatitis C infection.
13. Symptoms:
- Purpura.
- Joint pains.
- Kidney issues (hematuria, proteinuria).
- Monitor for kidney problems.
- Help coordinate antiviral therapy for Hepatitis C.
- Monitor for cold-induced symptoms (cryoglobulins precipitate in cold).
- --
Beyond the Tutorial
Nursing Actions Across All Vasculitides
1. Monitor for systemic signs of worsening disease:
- Decreased urine output.
- New respiratory symptoms.
- Severe abdominal pain or GI bleeding.
- Blood sugar elevation.
- Infection (masking early signs of sepsis).
- Osteoporosis prevention strategies (calcium and vitamin D).
- The importance of infection prevention.
- Adherence to medications even after symptoms improve.
- Monitoring and reporting any new organ-related symptoms (e.g., hematuria, chest pain, dyspnea).
