NCLEX - Medium & Variable Vessel Vasculitis
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Here are key facts for NCLEX from the Medium & Variable Size Vessel Vasculitis tutorial, as well as points of interest at the end of this document that are not directly addressed in this tutorial but should help you prepare for the boards. See the tutorial notes for further details and relevant links.
- --
VITAL FOR NCLEX
General Concepts of Vasculitis
1. Vasculitis means inflammation of blood vessels causing ischemia, organ damage, and tissue necrosis.
2. Common general symptoms include fever, fatigue, weakness, joint pains, and weight loss.
3. First-line treatment for most vasculitides involves corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and prevent organ damage.
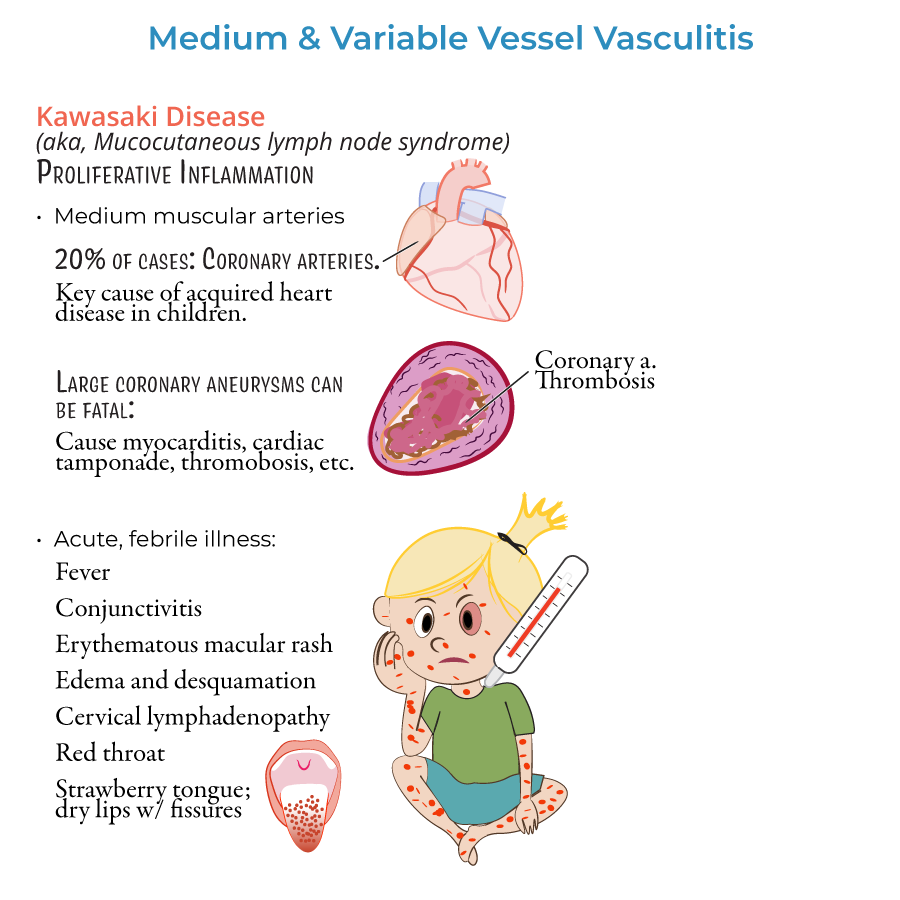
Kawasaki Disease (Most NCLEX-Relevant Vasculitis)
4. Kawasaki disease primarily affects young children under age 5 and involves medium-sized arteries, especially the coronary arteries.
5. Key signs and symptoms:
- Persistent fever for ≥5 days
- Bilateral conjunctival redness (without pus)
- Strawberry tongue, red cracked lips
- Swollen, red hands and feet with later skin peeling (desquamation)
- Polymorphous rash
- Cervical lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes)
- Administer IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) as ordered
- Administer high-dose aspirin
- Monitor closely for fever resolution and cardiac complications (arrhythmias, myocardial infarction)

Nursing Priorities for Kawasaki Disease
9. Assess for new chest pain, arrhythmias, or sudden breathlessness — these may indicate a coronary complication.
10. Monitor vital signs closely during IVIG infusion for infusion reactions.
11. Educate parents about the importance of follow-up echocardiograms and medication compliance.
- --
HIGH YIELD
Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)
1. Polyarteritis nodosa affects medium-sized arteries, leading to systemic ischemia.
2. Key symptoms may include:
- Hypertension
- Abdominal pain (mesenteric ischemia)
- Skin ulcers or purplish rashes (livedo reticularis)
- Peripheral neuropathy (weakness or numbness in hands/feet)
- Monitoring for blood pressure changes
- Watching for abdominal tenderness or GI bleeding
- Preventing infections during immunosuppressive therapy
Behçet Disease
5. Behçet disease causes recurrent painful mouth and genital sores, eye inflammation, and skin lesions.
6. Patients may experience blurred vision or eye pain — report to provider urgently to prevent blindness.
7. Nursing role:
- Teach about flare management with corticosteroids.
- Encourage compliance with routine eye exams.
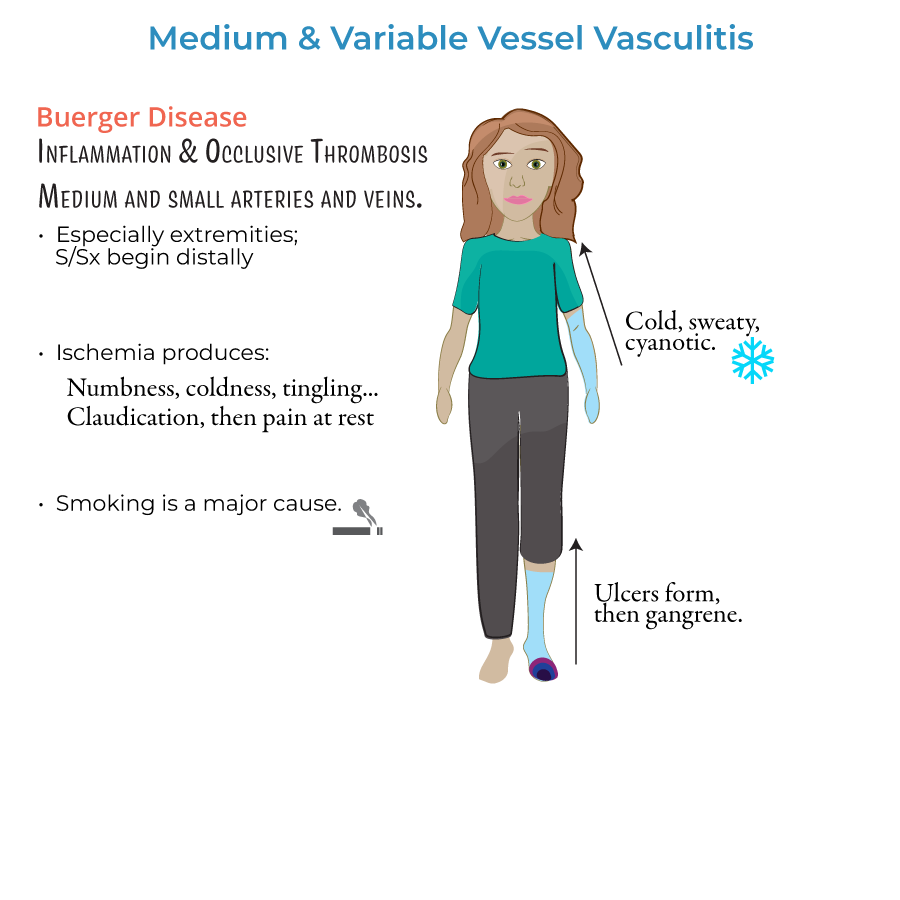
Buerger Disease (Thromboangiitis Obliterans)
8. Buerger disease involves small and medium arteries mainly in young male smokers.
9. Symptoms include:
- Numbness and coldness in fingers and toes
- Ulcers, pain at rest, gangrene
- Stress smoking cessation as essential for disease control.
- Monitor for signs of tissue ischemia (cold, blue extremities).

- --
Beyond the Tutorial
Critical Nursing Actions
1. In Kawasaki disease:
- Initiate IVIG and aspirin promptly once ordered.
- Educate parents about delayed vaccination schedules (no live vaccines for 11 months after IVIG).
- Monitor for hyperglycemia, infections, and GI bleeding.
- Provide teaching on hand hygiene and infection prevention.
- Monitor for kidney function decline (e.g., decreasing urine output, rising creatinine).
- Check skin for signs of ulceration or necrosis.
- Teach about proper foot care to prevent ulcers and amputations.
