
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
Liver Anatomy
Here we'll learn about the liver, which is the largest gland and visceral organ in the body; in the adult, it weighs about three pounds.
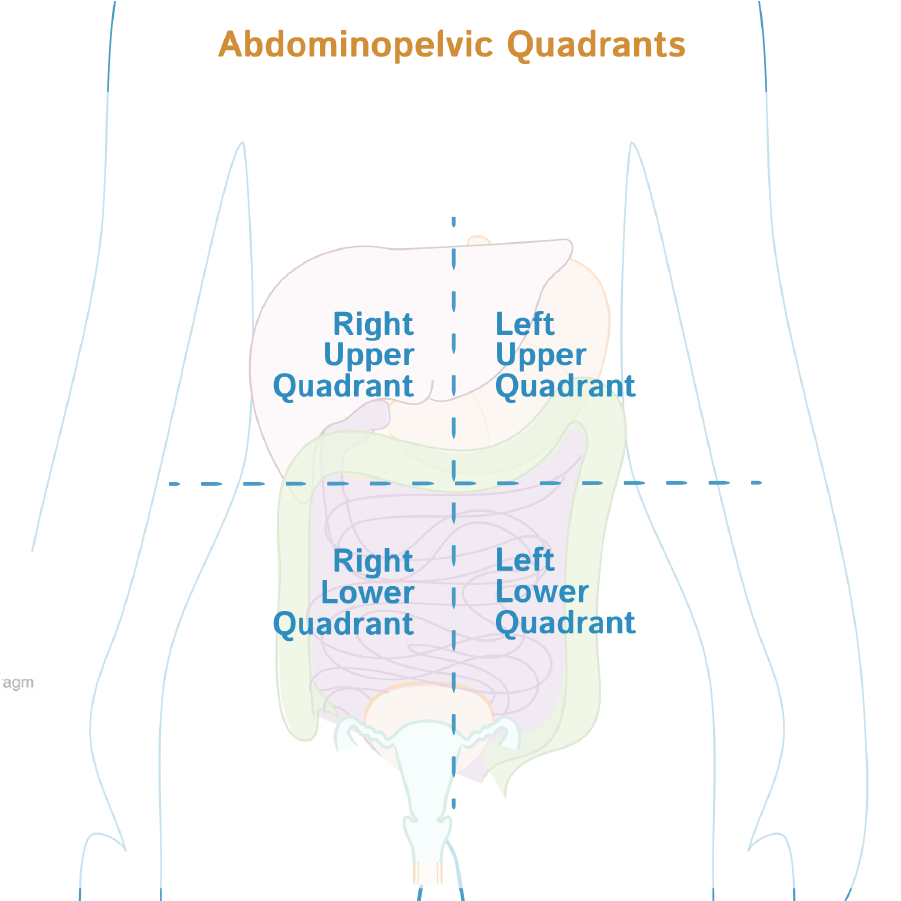
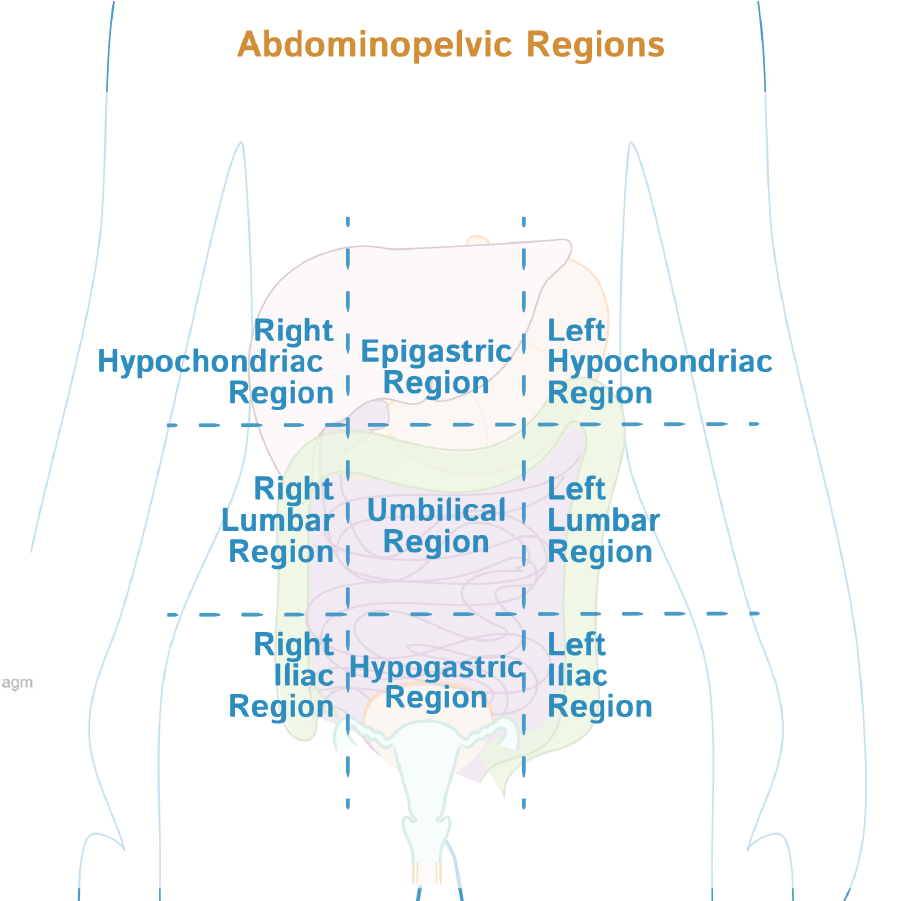
The liver is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen; it lies under the diaphragm to the right of the stomach, and its right side is covered by the rib cage, which helps to protect it.
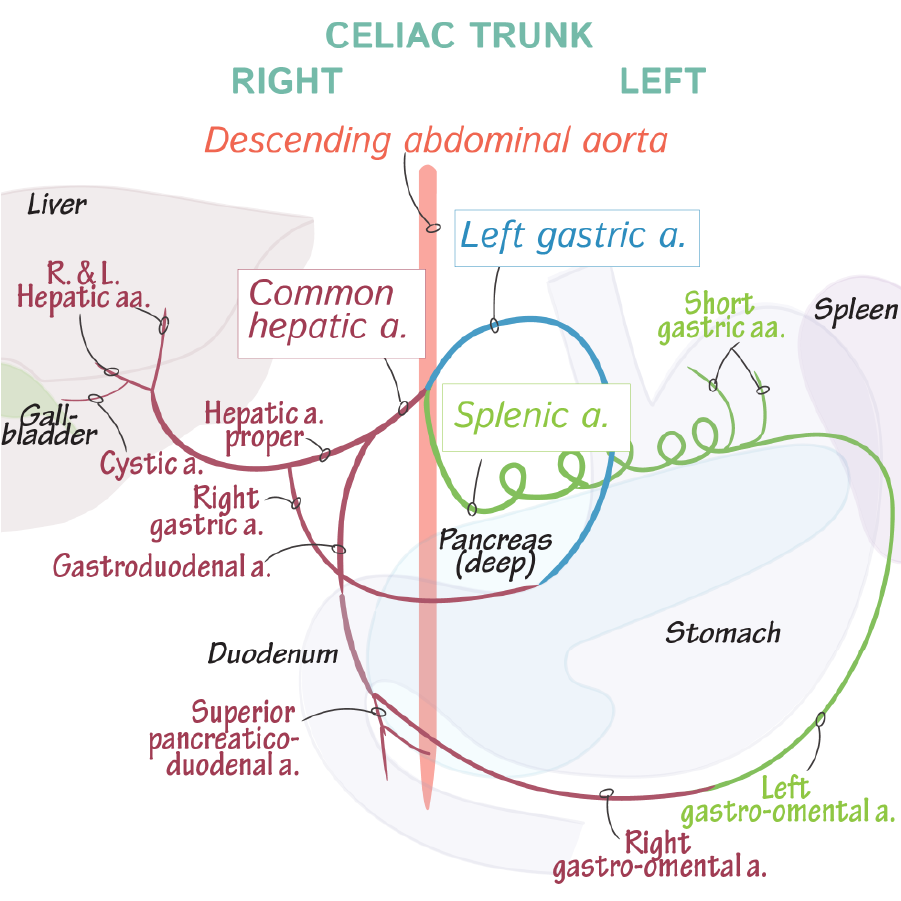 The hepatic portal system sends blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver for filtration.
Filtered blood leaves the liver via the hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
We show the nearby diaphragm and kidney; the wedge-shaped liver is under the diaphragm.
Two surfaces of the liver, demarcated by the inferior border:
The diaphragmatic surface is adjacent to the diaphragm, and comprises the anterior, superior, and posterior surfaces of the liver.
The visceral surface is adjacent to the abdominal viscera; it comprises the posteroinferior surface.
The outer cover of the liver comprises a dense, fibrous capsule (Glisson's capsule).
Most of the liver is also covered in a layer of visceral peritoneum, which helps to reduce friction against other structures. The posterior aspect of the diaphragmatic surface is not covered in peritoneum, so we call it the "bare area."
The hepatic portal system sends blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver for filtration.
Filtered blood leaves the liver via the hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
We show the nearby diaphragm and kidney; the wedge-shaped liver is under the diaphragm.
Two surfaces of the liver, demarcated by the inferior border:
The diaphragmatic surface is adjacent to the diaphragm, and comprises the anterior, superior, and posterior surfaces of the liver.
The visceral surface is adjacent to the abdominal viscera; it comprises the posteroinferior surface.
The outer cover of the liver comprises a dense, fibrous capsule (Glisson's capsule).
Most of the liver is also covered in a layer of visceral peritoneum, which helps to reduce friction against other structures. The posterior aspect of the diaphragmatic surface is not covered in peritoneum, so we call it the "bare area."
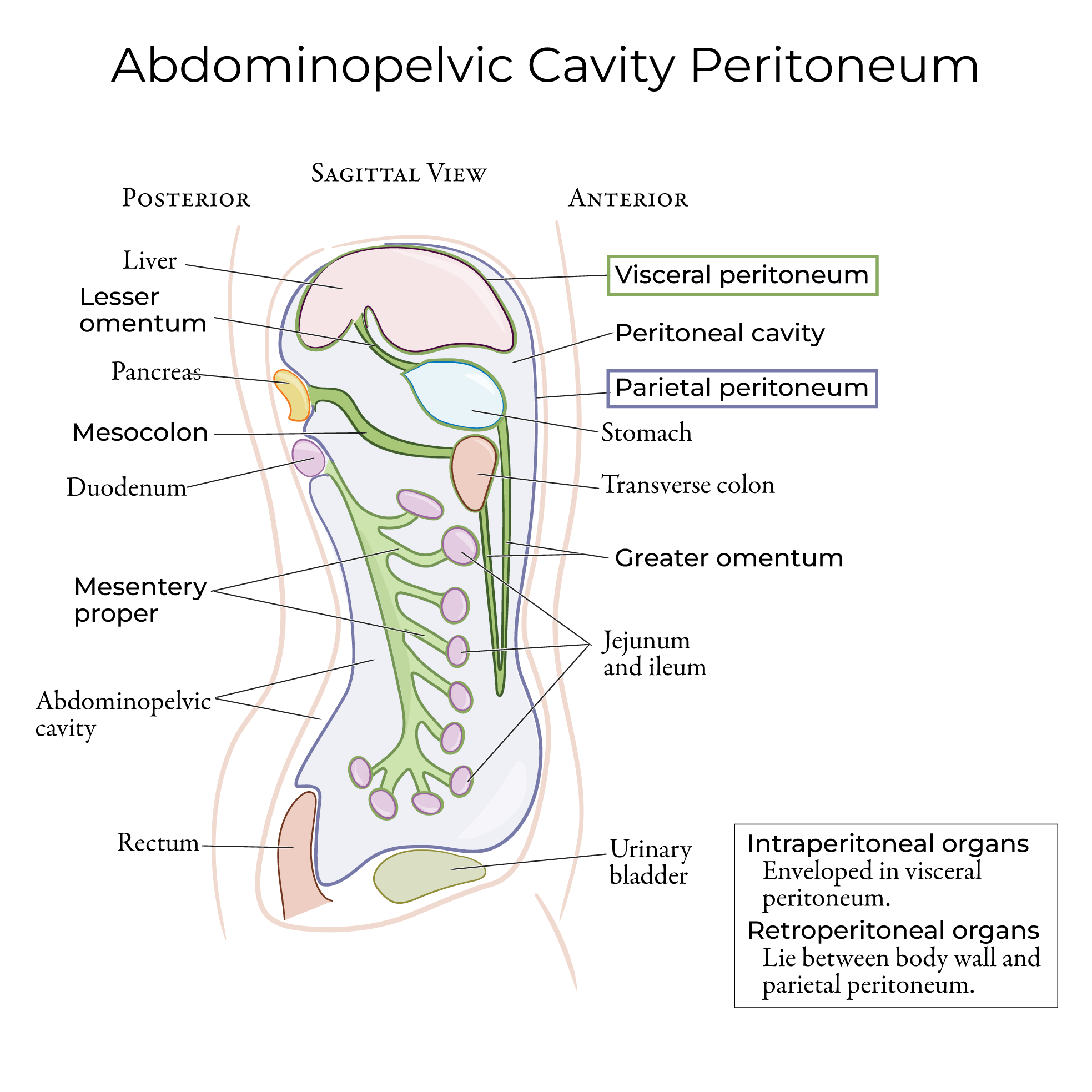 The peritoneum folds upon itself to create ligaments that anchor the liver in place.
We indicate the anterior and posterior layers of the coronary ligament, which attaches the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm and forms the edges of the bare area.
The subphrenic recess is the potential space between the liver and the diaphragm.
The subhepatic space is the area inferior to the liver.
The hepatorenal recess (aka Morison's pouch) is a subdivision of the right subhepatic space between the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
We show the diaphragm and the liver below it.
Peeking out from the inferior border, we show the tip of the gallbladder, which stores bile produced by the liver.
The anterior coronary ligament anchors the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm; the right and left triangular ligaments form where the anterior and posterior coronary ligaments meet laterally.
The falciform ligament anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and the diaphragm; it superficially divides the anterior liver into right and left lobes. Notice that the right lobe is significantly larger.
Within the inferior border of the falciform ligament, we see the round ligament; this is a remnant of the umbilical vein.
Ligaments that are formed from fetal remnants are known as "true" ligaments, as opposed to those that are created by folds of peritoneum, such as the coronary ligaments, which are known as "false" ligaments.
The inferior vena cava, gallbladder, and ligaments divide this surface into four lobes.
Two structures roughly align in the right sagittal fissure:
Superiorly, the inferior vena cava; filtered blood exits the liver via the right and left hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
Inferiorly, the gallbladder.
Now, show the ligaments:
The posterior coronary ligament demarcates the bare area of the liver.
The right and left triangular ligaments are formed where the anterior and posterior coronary ligaments meet.
Superiorly, label the top of the falciform ligament, which, as we've shown previously, travels along the anterior surface of the liver.
The left sagittal fissure (aka umbilical fissure) is a groove formed by the following two fissures:
Superiorly, the fissure for the ligamentum venosum, which contains the ligamentum venosum. The ligamentum venosum is the fibrous remnant of the fetal ductus venosum, which shunted blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver.
Inferiorly, the fissure for the ligamentum teres and the ligamentum teres, aka the round ligament of the liver. We saw a portion of the round ligament in the falciform ligament on the anterior surface of the liver.
The porta hepatis, aka transverse hepatic fissure or the hilum of the liver; this is where the hepatic portal vein and artery enter the liver and where the hepatic ducts exit the liver (nervous and lymphatic structures also pass through here).
Recall that the artery, vein, and bile duct, collectively known as the portal triad, travel to and from the liver within the lesser omentum (specifically within the hepatoduodenal ligament).
With these structures in place, we can label the 4 anatomical lobes:
The left lobe is bound by the left border of the liver and the fissures for the ligamentum venosum and ligamentum teres.
To the right of the fissure for the ligamentum venosum is the caudate lobe, which is bound on the right side by the inferior vena cava.
To the right of the fissure for the ligamentum teres, is the quadrate lobe, which is bound on the right side by the gallbladder.
Lastly, we label the right lobe.
Notice that we can roughly describe the lobes as situated around a letter H:
The gallbladder and round ligament of the liver comprise the inferior parts of the vertical legs; the inferior vena cava and ligamentum venosum are the superior legs. The porta hepatis is the horizontal bar of the H.
Be aware that surgeons subdivide the liver into 8 segments based upon vascular and lymphatic structures; this segmentation allows for surgical removal of liver sections with less risk of vascular damage.
The peritoneum folds upon itself to create ligaments that anchor the liver in place.
We indicate the anterior and posterior layers of the coronary ligament, which attaches the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm and forms the edges of the bare area.
The subphrenic recess is the potential space between the liver and the diaphragm.
The subhepatic space is the area inferior to the liver.
The hepatorenal recess (aka Morison's pouch) is a subdivision of the right subhepatic space between the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
We show the diaphragm and the liver below it.
Peeking out from the inferior border, we show the tip of the gallbladder, which stores bile produced by the liver.
The anterior coronary ligament anchors the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm; the right and left triangular ligaments form where the anterior and posterior coronary ligaments meet laterally.
The falciform ligament anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and the diaphragm; it superficially divides the anterior liver into right and left lobes. Notice that the right lobe is significantly larger.
Within the inferior border of the falciform ligament, we see the round ligament; this is a remnant of the umbilical vein.
Ligaments that are formed from fetal remnants are known as "true" ligaments, as opposed to those that are created by folds of peritoneum, such as the coronary ligaments, which are known as "false" ligaments.
The inferior vena cava, gallbladder, and ligaments divide this surface into four lobes.
Two structures roughly align in the right sagittal fissure:
Superiorly, the inferior vena cava; filtered blood exits the liver via the right and left hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
Inferiorly, the gallbladder.
Now, show the ligaments:
The posterior coronary ligament demarcates the bare area of the liver.
The right and left triangular ligaments are formed where the anterior and posterior coronary ligaments meet.
Superiorly, label the top of the falciform ligament, which, as we've shown previously, travels along the anterior surface of the liver.
The left sagittal fissure (aka umbilical fissure) is a groove formed by the following two fissures:
Superiorly, the fissure for the ligamentum venosum, which contains the ligamentum venosum. The ligamentum venosum is the fibrous remnant of the fetal ductus venosum, which shunted blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver.
Inferiorly, the fissure for the ligamentum teres and the ligamentum teres, aka the round ligament of the liver. We saw a portion of the round ligament in the falciform ligament on the anterior surface of the liver.
The porta hepatis, aka transverse hepatic fissure or the hilum of the liver; this is where the hepatic portal vein and artery enter the liver and where the hepatic ducts exit the liver (nervous and lymphatic structures also pass through here).
Recall that the artery, vein, and bile duct, collectively known as the portal triad, travel to and from the liver within the lesser omentum (specifically within the hepatoduodenal ligament).
With these structures in place, we can label the 4 anatomical lobes:
The left lobe is bound by the left border of the liver and the fissures for the ligamentum venosum and ligamentum teres.
To the right of the fissure for the ligamentum venosum is the caudate lobe, which is bound on the right side by the inferior vena cava.
To the right of the fissure for the ligamentum teres, is the quadrate lobe, which is bound on the right side by the gallbladder.
Lastly, we label the right lobe.
Notice that we can roughly describe the lobes as situated around a letter H:
The gallbladder and round ligament of the liver comprise the inferior parts of the vertical legs; the inferior vena cava and ligamentum venosum are the superior legs. The porta hepatis is the horizontal bar of the H.
Be aware that surgeons subdivide the liver into 8 segments based upon vascular and lymphatic structures; this segmentation allows for surgical removal of liver sections with less risk of vascular damage.
 Hepatic lobules are the functional units of the liver.
Classic Lobule Model:
A central, aka, hepatic, venule with peripheral portal triads, aka, portal tracts and the smaller vessels that connect them.
The liver tissue comprises rows, aka, plates, of hepatocytes radiating from the central venule. Blood travels between the plates, and bile travels within bile canaliculi.
Ultimately, bile drains to the hepatic ducts and exits the liver via the biliary system.
Filtered, deoxygenated blood drains to the hepatic veins and to the inferior vena cava to re-enter general circulation.
Liver Histology
Hepatic lobules are the functional units of the liver.
Classic Lobule Model:
A central, aka, hepatic, venule with peripheral portal triads, aka, portal tracts and the smaller vessels that connect them.
The liver tissue comprises rows, aka, plates, of hepatocytes radiating from the central venule. Blood travels between the plates, and bile travels within bile canaliculi.
Ultimately, bile drains to the hepatic ducts and exits the liver via the biliary system.
Filtered, deoxygenated blood drains to the hepatic veins and to the inferior vena cava to re-enter general circulation.
Liver Histology



Liver Functions
- Bile production; bile breaks down lipids in the small intestine.
- Filtration and detoxification of the blood
- Blood plasma protein synthesis
- Nutrient metabolism
- Hormone secretion and modification
- Vitamin and nutrient storage.
Anatomical Context


Blood Supply
Arterial blood supply to the liver is provided by the proper hepatic artery, a branch of the common hepatic artery.
 The hepatic portal system sends blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver for filtration.
Filtered blood leaves the liver via the hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
The hepatic portal system sends blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver for filtration.
Filtered blood leaves the liver via the hepatic veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava.
Innervation
The liver is innervated by the anterior and posterior hepatic nervous plexuses, which comprises sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that travel with the hepatic artery and portal vein.
Right lateral view
 The peritoneum folds upon itself to create ligaments that anchor the liver in place.
We indicate the anterior and posterior layers of the coronary ligament, which attaches the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm and forms the edges of the bare area.
The subphrenic recess is the potential space between the liver and the diaphragm.
The subhepatic space is the area inferior to the liver.
The hepatorenal recess (aka Morison's pouch) is a subdivision of the right subhepatic space between the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
The peritoneum folds upon itself to create ligaments that anchor the liver in place.
We indicate the anterior and posterior layers of the coronary ligament, which attaches the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm and forms the edges of the bare area.
The subphrenic recess is the potential space between the liver and the diaphragm.
The subhepatic space is the area inferior to the liver.
The hepatorenal recess (aka Morison's pouch) is a subdivision of the right subhepatic space between the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
Anterior View
Posterior View

Hepatic Lobule
CT Scans





