
Start your One-Week Free Trial
Already subscribed? Log in »
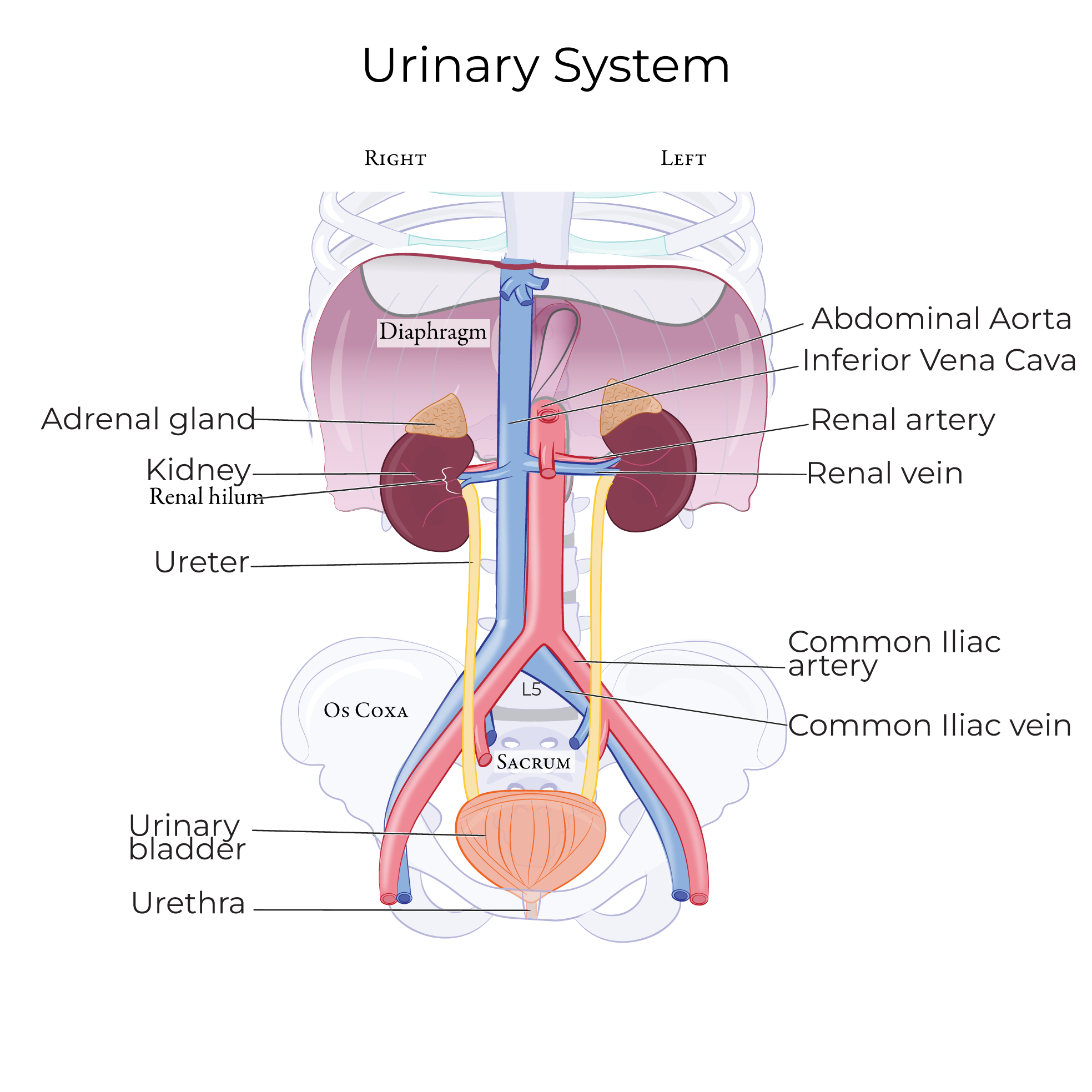
Kidney Anatomy with Vascular Supply
Here we'll learn the anatomy of the kidneys, which filter wastes, toxins, and excess water from the blood to produce urine. Urine is produced and concentrated in the kidneys, then exits the kidneys via the ureters and is stored in the urinary bladder.
The kidneys are retroperitoneal.
 We first outline the left kidney in coronal section, and we label the inferior and superior poles.
Though not shown, remember that the adrenal (aka suprarenal) glands sit on the superior poles of the kidneys
The outermost covering is the fibrous capsule (aka renal capsule), it is a layer of protective connective tissue.
The renal hilum is on the medial side of the kidney; this is the cleft where the renal arteries, veins, nerves, and ureters enter and exit the kidney.
The hilum is continuous with the renal sinus, which is a cavity that holds fat, blood vessels, and the proximal ends of the ureters.
Next, we show some representative renal pyramids so that their apexes are in the renal sinus and their wide bases point towards the renal capsule. Adult kidneys have 8-15 renal pyramids.
The renal pyramids comprise urine-collecting tubules and ducts, which gives them a striated appearance.
Collectively, the renal pyramids make up the renal medulla.
The area outside the medulla is the renal cortex; the cortex extends between the pyramids as renal columns.
The corticomedullary junction is where the wide base of the pyramid meets the cortex.
A renal lobe comprises a single renal pyramid and the cortex that surrounds it.
Let's show some representative nephrons, which are the functional urine-producing components of the kidneys. In adults, the paired kidneys house approximately 2.5 million nephrons.
We first outline the left kidney in coronal section, and we label the inferior and superior poles.
Though not shown, remember that the adrenal (aka suprarenal) glands sit on the superior poles of the kidneys
The outermost covering is the fibrous capsule (aka renal capsule), it is a layer of protective connective tissue.
The renal hilum is on the medial side of the kidney; this is the cleft where the renal arteries, veins, nerves, and ureters enter and exit the kidney.
The hilum is continuous with the renal sinus, which is a cavity that holds fat, blood vessels, and the proximal ends of the ureters.
Next, we show some representative renal pyramids so that their apexes are in the renal sinus and their wide bases point towards the renal capsule. Adult kidneys have 8-15 renal pyramids.
The renal pyramids comprise urine-collecting tubules and ducts, which gives them a striated appearance.
Collectively, the renal pyramids make up the renal medulla.
The area outside the medulla is the renal cortex; the cortex extends between the pyramids as renal columns.
The corticomedullary junction is where the wide base of the pyramid meets the cortex.
A renal lobe comprises a single renal pyramid and the cortex that surrounds it.
Let's show some representative nephrons, which are the functional urine-producing components of the kidneys. In adults, the paired kidneys house approximately 2.5 million nephrons.
 Juxtamedullary nephrons begin in the cortex and extends deep into the medulla.
Cortical nephrons lie almost entirely in the cortex.
Cortical nephrons comprise over 80% of the nephrons in the kidney, but juxtamedullary nephrons, with their longer loops, play an important role in urine concentration.
Now, let's trace the path of urine from the pyramids to the ureters.
Start in the renal pyramid; urine travels through the collecting ducts to the apex of the pyramid, which is called the renal papilla.
Each renal papilla drains urine into a minor calyx; minor calyxes converge to from major calyces.
The major calyces converge at the renal pelvis, which is the wide, flattened opening of the ureter, which carries the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Next, let's show how blood travels through the kidney to reach the nephrons for filtration.
The renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum; the renal arteries branch directly off the abdominal aorta.
Juxtamedullary nephrons begin in the cortex and extends deep into the medulla.
Cortical nephrons lie almost entirely in the cortex.
Cortical nephrons comprise over 80% of the nephrons in the kidney, but juxtamedullary nephrons, with their longer loops, play an important role in urine concentration.
Now, let's trace the path of urine from the pyramids to the ureters.
Start in the renal pyramid; urine travels through the collecting ducts to the apex of the pyramid, which is called the renal papilla.
Each renal papilla drains urine into a minor calyx; minor calyxes converge to from major calyces.
The major calyces converge at the renal pelvis, which is the wide, flattened opening of the ureter, which carries the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Next, let's show how blood travels through the kidney to reach the nephrons for filtration.
The renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum; the renal arteries branch directly off the abdominal aorta.
 Within the renal sinus, the renal artery gives rise to segmental arteries, which then give rise to interlobar arteries. Interlobar arteries travel within the renal columns along the sides of the pyramids.
At the corticomedullary junction, interlobar arteries give rise to arcuate arteries; these branches from arcs over the bases of the pyramids.
The arcuate arteries give rise to multiple interlobular arteries, which radiate through the cortex (hence their alternative name, cortical radiate arteries).
The interlobular arteries give rise to afferent arterioles that travel to the first part of the nephron, called the glomerulus, where blood is filtered.
After blood passes through the vessels surrounding the nephron, it travels through a system of veins.
The names and pathways of these veins mirror the arteries (with one exception, there's no segmental vein). Thus, we will omit the veins in our diagram for simplicity. Ultimately, blood will exit the kidney via the renal vein, which drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
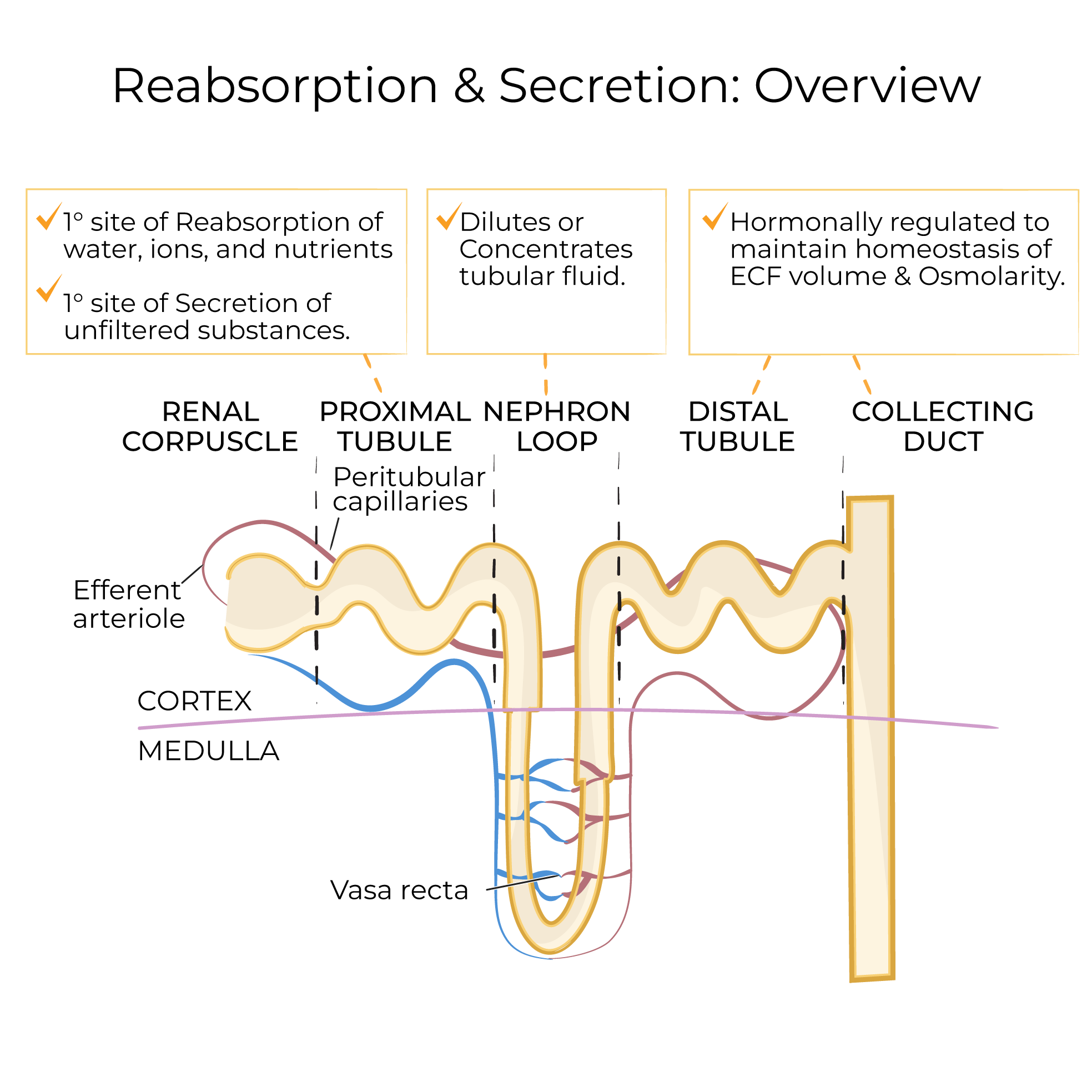
Let's draw a renal lobe with a juxtamedullary nephron to get a better view of the relationship between the renal vasculature and nephrons.
We show the renal cortex and a renal pyramid.
Then, we draw a juxtamedullary nephron:
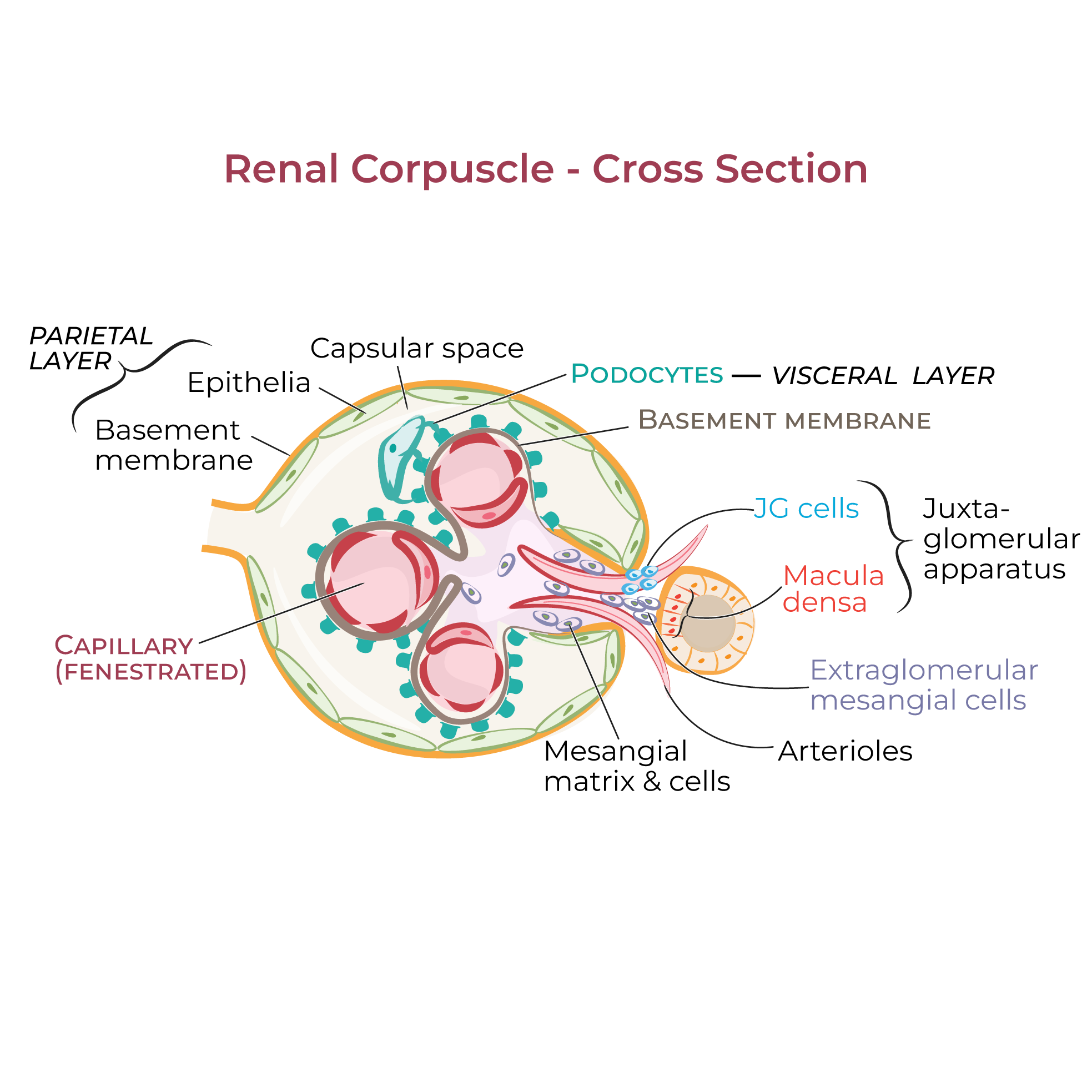
The first section is the renal corpuscle; show that it comprises a ball-shaped glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) that houses a tuft of specialized capillaries called the glomerulus.
The next segment of the nephron is the proximal convoluted tubule – this segment is proximal (next to the glomerular capsule) and is "convoluted" it twists and wraps around itself in the renal cortex.
The next segment is the nephron loop (aka the loop of Henle); we can further subdivide the loop into descending and ascending limbs.
The distal convoluted tubule – it's distal to the glomerular capsule, and has a twisted appearance.
The distal convoluted tubule is continuous with the collecting duct, which drains multiple nephrons.
The collecting ducts carry urine through the pyramid to the renal papilla, where urine from multiple ducts collects before passing through the minor and major calyces.
Within the renal sinus, the renal artery gives rise to segmental arteries, which then give rise to interlobar arteries. Interlobar arteries travel within the renal columns along the sides of the pyramids.
At the corticomedullary junction, interlobar arteries give rise to arcuate arteries; these branches from arcs over the bases of the pyramids.
The arcuate arteries give rise to multiple interlobular arteries, which radiate through the cortex (hence their alternative name, cortical radiate arteries).
The interlobular arteries give rise to afferent arterioles that travel to the first part of the nephron, called the glomerulus, where blood is filtered.
After blood passes through the vessels surrounding the nephron, it travels through a system of veins.
The names and pathways of these veins mirror the arteries (with one exception, there's no segmental vein). Thus, we will omit the veins in our diagram for simplicity. Ultimately, blood will exit the kidney via the renal vein, which drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
Let's draw a renal lobe with a juxtamedullary nephron to get a better view of the relationship between the renal vasculature and nephrons.
We show the renal cortex and a renal pyramid.
Then, we draw a juxtamedullary nephron:
The first section is the renal corpuscle; show that it comprises a ball-shaped glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) that houses a tuft of specialized capillaries called the glomerulus.
The next segment of the nephron is the proximal convoluted tubule – this segment is proximal (next to the glomerular capsule) and is "convoluted" it twists and wraps around itself in the renal cortex.
The next segment is the nephron loop (aka the loop of Henle); we can further subdivide the loop into descending and ascending limbs.
The distal convoluted tubule – it's distal to the glomerular capsule, and has a twisted appearance.
The distal convoluted tubule is continuous with the collecting duct, which drains multiple nephrons.
The collecting ducts carry urine through the pyramid to the renal papilla, where urine from multiple ducts collects before passing through the minor and major calyces.
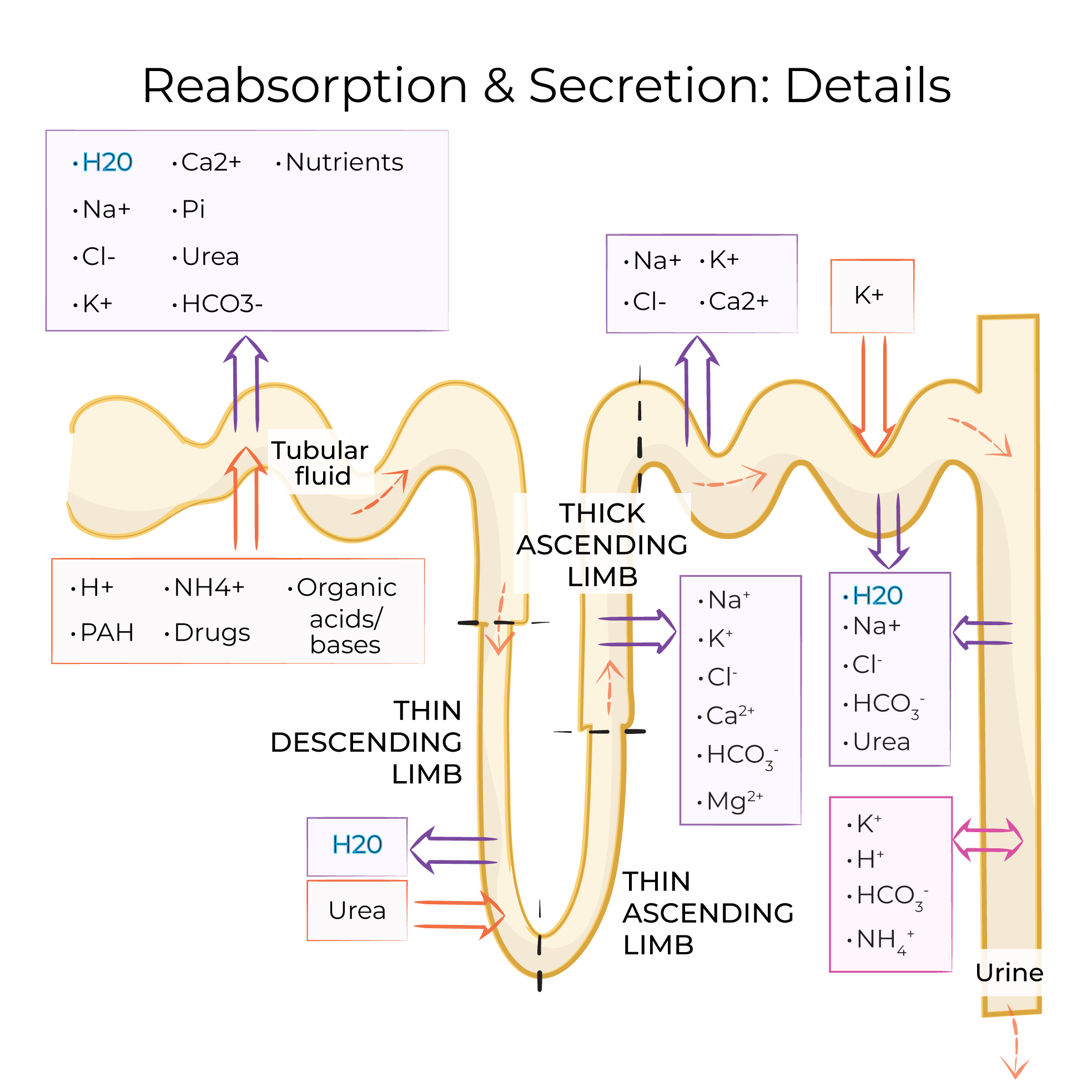 With this in place, we can show the vasculature.
The interlobar artery and vein travel the length of the pyramid; they become the arcuate artery and vein when they arch over the base of the pyramid.
The arcuate vessels give rise to the interlobular artery and vein; the interlobular artery gives off the afferent arteriole.
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerular capsule of the nephron and is continuous with the glomerulus, which is a specialized tuft of capillaries where filtration begins. Together, the glomerulus and the capsule comprise the renal corpuscle.
With this in place, we can show the vasculature.
The interlobar artery and vein travel the length of the pyramid; they become the arcuate artery and vein when they arch over the base of the pyramid.
The arcuate vessels give rise to the interlobular artery and vein; the interlobular artery gives off the afferent arteriole.
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerular capsule of the nephron and is continuous with the glomerulus, which is a specialized tuft of capillaries where filtration begins. Together, the glomerulus and the capsule comprise the renal corpuscle.
 Filtered blood exits the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole and enters the peritubular capillaries.
The peritubular capillaries are located in the renal cortex in close association with the nephron, allowing for additional fine-tuning of the urine. Be aware of intertextual variation on this point; some authors restrict the use of the name "peritubular capillaries" to cortical nephrons, and others do not.
In juxtamedually nephrons, blood travels alongside the nephron loop in the vasa recta. Oxygenated blood enters the vasa recta, gas exchange occurs along the length of the loop, and deoxygenated blood exits the vasa recta via the interlobular vein.
From the interlobular vein, blood travels through the venous network that mirrors the arterial network; ultimately, it exits the kidney via the renal vein at the hilum and is returned to the inferior vena cava.
Kidney Stones
Acute Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease
Renal Artery Stenosis
Filtered blood exits the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole and enters the peritubular capillaries.
The peritubular capillaries are located in the renal cortex in close association with the nephron, allowing for additional fine-tuning of the urine. Be aware of intertextual variation on this point; some authors restrict the use of the name "peritubular capillaries" to cortical nephrons, and others do not.
In juxtamedually nephrons, blood travels alongside the nephron loop in the vasa recta. Oxygenated blood enters the vasa recta, gas exchange occurs along the length of the loop, and deoxygenated blood exits the vasa recta via the interlobular vein.
From the interlobular vein, blood travels through the venous network that mirrors the arterial network; ultimately, it exits the kidney via the renal vein at the hilum and is returned to the inferior vena cava.
Kidney Stones
Acute Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease
Renal Artery Stenosis

Renal Functions
- Filtration and excretion remove wastes and toxins from the blood and regulates ion and acid-base balance.
- By regulating how much water is excreted in the urine, the kidneys play a role in maintaining blood volume and, therefore, pressure.
- The kidneys respond to low oxygen levels (hypoxia) by releasing erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
- The kidneys also convert vitamin D to its active form; vitamin D is necessary for bone growth.
Kidney in Coronal Section
 Juxtamedullary nephrons begin in the cortex and extends deep into the medulla.
Cortical nephrons lie almost entirely in the cortex.
Cortical nephrons comprise over 80% of the nephrons in the kidney, but juxtamedullary nephrons, with their longer loops, play an important role in urine concentration.
Now, let's trace the path of urine from the pyramids to the ureters.
Start in the renal pyramid; urine travels through the collecting ducts to the apex of the pyramid, which is called the renal papilla.
Each renal papilla drains urine into a minor calyx; minor calyxes converge to from major calyces.
The major calyces converge at the renal pelvis, which is the wide, flattened opening of the ureter, which carries the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Next, let's show how blood travels through the kidney to reach the nephrons for filtration.
The renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum; the renal arteries branch directly off the abdominal aorta.
Juxtamedullary nephrons begin in the cortex and extends deep into the medulla.
Cortical nephrons lie almost entirely in the cortex.
Cortical nephrons comprise over 80% of the nephrons in the kidney, but juxtamedullary nephrons, with their longer loops, play an important role in urine concentration.
Now, let's trace the path of urine from the pyramids to the ureters.
Start in the renal pyramid; urine travels through the collecting ducts to the apex of the pyramid, which is called the renal papilla.
Each renal papilla drains urine into a minor calyx; minor calyxes converge to from major calyces.
The major calyces converge at the renal pelvis, which is the wide, flattened opening of the ureter, which carries the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Next, let's show how blood travels through the kidney to reach the nephrons for filtration.
The renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum; the renal arteries branch directly off the abdominal aorta.
 Within the renal sinus, the renal artery gives rise to segmental arteries, which then give rise to interlobar arteries. Interlobar arteries travel within the renal columns along the sides of the pyramids.
At the corticomedullary junction, interlobar arteries give rise to arcuate arteries; these branches from arcs over the bases of the pyramids.
The arcuate arteries give rise to multiple interlobular arteries, which radiate through the cortex (hence their alternative name, cortical radiate arteries).
The interlobular arteries give rise to afferent arterioles that travel to the first part of the nephron, called the glomerulus, where blood is filtered.
After blood passes through the vessels surrounding the nephron, it travels through a system of veins.
The names and pathways of these veins mirror the arteries (with one exception, there's no segmental vein). Thus, we will omit the veins in our diagram for simplicity. Ultimately, blood will exit the kidney via the renal vein, which drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
Within the renal sinus, the renal artery gives rise to segmental arteries, which then give rise to interlobar arteries. Interlobar arteries travel within the renal columns along the sides of the pyramids.
At the corticomedullary junction, interlobar arteries give rise to arcuate arteries; these branches from arcs over the bases of the pyramids.
The arcuate arteries give rise to multiple interlobular arteries, which radiate through the cortex (hence their alternative name, cortical radiate arteries).
The interlobular arteries give rise to afferent arterioles that travel to the first part of the nephron, called the glomerulus, where blood is filtered.
After blood passes through the vessels surrounding the nephron, it travels through a system of veins.
The names and pathways of these veins mirror the arteries (with one exception, there's no segmental vein). Thus, we will omit the veins in our diagram for simplicity. Ultimately, blood will exit the kidney via the renal vein, which drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
Juxtamedullary nephron
 With this in place, we can show the vasculature.
The interlobar artery and vein travel the length of the pyramid; they become the arcuate artery and vein when they arch over the base of the pyramid.
The arcuate vessels give rise to the interlobular artery and vein; the interlobular artery gives off the afferent arteriole.
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerular capsule of the nephron and is continuous with the glomerulus, which is a specialized tuft of capillaries where filtration begins. Together, the glomerulus and the capsule comprise the renal corpuscle.
With this in place, we can show the vasculature.
The interlobar artery and vein travel the length of the pyramid; they become the arcuate artery and vein when they arch over the base of the pyramid.
The arcuate vessels give rise to the interlobular artery and vein; the interlobular artery gives off the afferent arteriole.
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerular capsule of the nephron and is continuous with the glomerulus, which is a specialized tuft of capillaries where filtration begins. Together, the glomerulus and the capsule comprise the renal corpuscle.
 Filtered blood exits the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole and enters the peritubular capillaries.
The peritubular capillaries are located in the renal cortex in close association with the nephron, allowing for additional fine-tuning of the urine. Be aware of intertextual variation on this point; some authors restrict the use of the name "peritubular capillaries" to cortical nephrons, and others do not.
In juxtamedually nephrons, blood travels alongside the nephron loop in the vasa recta. Oxygenated blood enters the vasa recta, gas exchange occurs along the length of the loop, and deoxygenated blood exits the vasa recta via the interlobular vein.
From the interlobular vein, blood travels through the venous network that mirrors the arterial network; ultimately, it exits the kidney via the renal vein at the hilum and is returned to the inferior vena cava.
Filtered blood exits the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole and enters the peritubular capillaries.
The peritubular capillaries are located in the renal cortex in close association with the nephron, allowing for additional fine-tuning of the urine. Be aware of intertextual variation on this point; some authors restrict the use of the name "peritubular capillaries" to cortical nephrons, and others do not.
In juxtamedually nephrons, blood travels alongside the nephron loop in the vasa recta. Oxygenated blood enters the vasa recta, gas exchange occurs along the length of the loop, and deoxygenated blood exits the vasa recta via the interlobular vein.
From the interlobular vein, blood travels through the venous network that mirrors the arterial network; ultimately, it exits the kidney via the renal vein at the hilum and is returned to the inferior vena cava.
Clinical Correlations



